초록접수 현황
| 20F-198 | 구연 발표 |
A prospective, randomized, non-inferiority study of poloxamer 407-based ropivacaine hydrogels versus continuous paravertebral block for acute postoperative pain following thoracoscopic pulmonary resection
Jae Hyun Jeon1, Yong Won Seong2, Ji Eun Han1, Sukki Cho1, Sanghoon Jheon1, and Kwhanmien Kim1
1. Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2. Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Purpose : We conducted a comparative study to evaluate the efficacy of local poloxamer 407-based ropivacaine hydrogel at wound site (Gel) and continuous paravertebral block (On-Q) for the management of postoperative pain following thoracoscopic pulmonary resection.
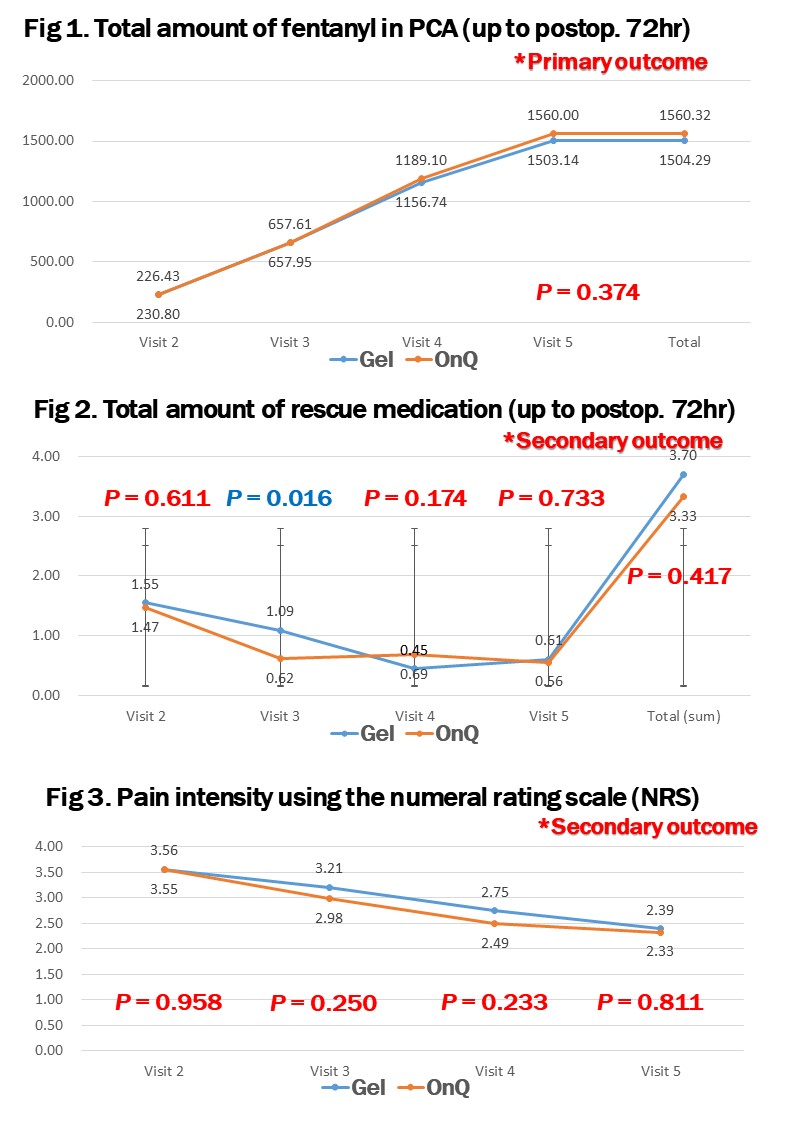
Methods : This prospective, randomized, non-inferiority study included 89 patients randomized into Gel (N = 44, poloxamer 407-based 0.75% ropivacaine 22.5mg) and On-Q (N = 45, 0.2% ropivacaine, 2mg/hour for 2 days) groups. Postoperative analgesia was induced in all cases with intravenous patients-controlled analgesia (PCA). The primary outcome measure was postoperative morphine consumption (non-inferiority margin; 197.4 mcg). Secondary measures were postoperative pain intensity and need for rescue analgesia.
Results : Both groups showed no difference in terms of age, sex, disease entity, operation time, chest tube indwelling time, and hospital stay. No statistically significant differences in the total postoperative fentanyl consumption were observed for the two groups (Gel group; 1504.29 ± 315.72, On-Q group; 1560.32 ± 274.81, p = 0.374). Pain intensity using the numeral rating scale (NRS) between the Gel and On-Q groups demonstrated no statistical differences (postoperative 6 hour; p = 0.958, 24 hour; p = 0.250, 48 hour; p = 0233, and 72 hour; p = 0.8110), and there was no statistically significant difference in frequency of analgesic rescue medication use (p = 0.417).
Conclusion : We confirm the non-inferiority of local poloxamer 407-based ropivacaine hydrogels compared with continuous paravertebral block for acute postoperative pain following thoracoscopic pulmonary resection.
Methods : This prospective, randomized, non-inferiority study included 89 patients randomized into Gel (N = 44, poloxamer 407-based 0.75% ropivacaine 22.5mg) and On-Q (N = 45, 0.2% ropivacaine, 2mg/hour for 2 days) groups. Postoperative analgesia was induced in all cases with intravenous patients-controlled analgesia (PCA). The primary outcome measure was postoperative morphine consumption (non-inferiority margin; 197.4 mcg). Secondary measures were postoperative pain intensity and need for rescue analgesia.
Results : Both groups showed no difference in terms of age, sex, disease entity, operation time, chest tube indwelling time, and hospital stay. No statistically significant differences in the total postoperative fentanyl consumption were observed for the two groups (Gel group; 1504.29 ± 315.72, On-Q group; 1560.32 ± 274.81, p = 0.374). Pain intensity using the numeral rating scale (NRS) between the Gel and On-Q groups demonstrated no statistical differences (postoperative 6 hour; p = 0.958, 24 hour; p = 0.250, 48 hour; p = 0233, and 72 hour; p = 0.8110), and there was no statistically significant difference in frequency of analgesic rescue medication use (p = 0.417).
Conclusion : We confirm the non-inferiority of local poloxamer 407-based ropivacaine hydrogels compared with continuous paravertebral block for acute postoperative pain following thoracoscopic pulmonary resection.
책임저자: Kwhanmien Kim
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
발표자: Jae Hyun Jeon, E-mail : fine1114@hanmail.net


