초록접수 현황
| 20F-030 | 구연 발표 |
Intraoperative tissue diagnosis with core needle biopsy for thoracic surgery
Hee Chul Yang, Moon Soo Kim, Jong Mog Lee
Center for Lung Cancer, Research Institute and Hospital, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea
Purpose : This study assessed the efficacy of intraoperative tissue diagnosis by frozen section using core needle biopsy specimen for intrathoracic lesions.
Methods : We retrospectively reviewed and analyzed the patients who had frozen section using the core needle biopsy specimens during operation for intrathoracic lesions.
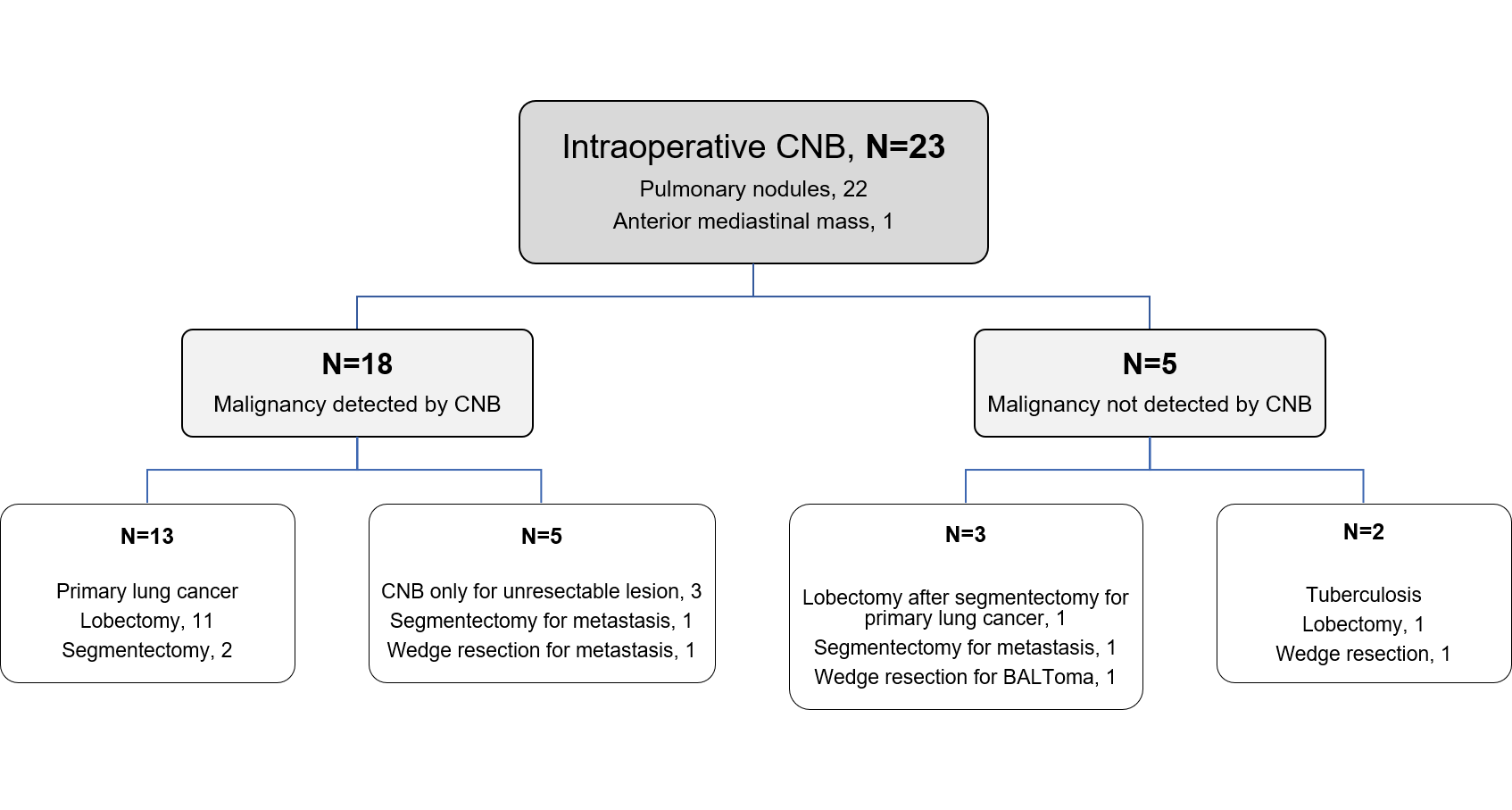
Results : Between January 2000 and January 2020, there were a total of 23 patients who had their specimen for frozen section by core needle biopsy of intrathoracic lesions. Except one case of anterior mediastinal mass, the others were for pulmonary nodules, fourteen cases (60.9%) out of which had undergone curative resection for primary lung cancer during the same operation. The core needle biopsy were done under video-assisted thoracoscopic approach in 14 cases (60.9%). The target lesions were mostly solid (n=21, 91.3%), centrally located (n=16, 69.6%), and the median size of the lesion was 28.5 mm (ranging from 10 to 90 mm). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of frozen section by core needle biopsy for intrathoracic lesions were 85.7%, 100.0%, 100%, and 40%, respectively. Among the 14 patients who underwent curative resection for primary lung cancer, none presented with ipsilateral pleural seeding during the follow-up period.
Conclusion : The core needle biopsy procedure may be considered for a method to obtain specimens for frozen section during the operation for intrathoracic lesions with solid feature and central location.
Methods : We retrospectively reviewed and analyzed the patients who had frozen section using the core needle biopsy specimens during operation for intrathoracic lesions.
Results : Between January 2000 and January 2020, there were a total of 23 patients who had their specimen for frozen section by core needle biopsy of intrathoracic lesions. Except one case of anterior mediastinal mass, the others were for pulmonary nodules, fourteen cases (60.9%) out of which had undergone curative resection for primary lung cancer during the same operation. The core needle biopsy were done under video-assisted thoracoscopic approach in 14 cases (60.9%). The target lesions were mostly solid (n=21, 91.3%), centrally located (n=16, 69.6%), and the median size of the lesion was 28.5 mm (ranging from 10 to 90 mm). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of frozen section by core needle biopsy for intrathoracic lesions were 85.7%, 100.0%, 100%, and 40%, respectively. Among the 14 patients who underwent curative resection for primary lung cancer, none presented with ipsilateral pleural seeding during the follow-up period.
Conclusion : The core needle biopsy procedure may be considered for a method to obtain specimens for frozen section during the operation for intrathoracic lesions with solid feature and central location.
책임저자: Jin-Ho Choi
Center for Lung Cancer, Research Institute and Hospital, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea
발표자: Jin-Ho Choi, E-mail : miracleho@gmail.com


