초록접수 현황
| 20F-022 | 구연 발표 |
Impact of Dual Cannulation on Visceral Malperfusion in Aortic Dissection Repair: Fluid Structural Interaction Analysis
Woon Heo1, Tae-Hoon Kim2, Hojin Ha3, Gyu-Han Lee3, Ha Lee2, Myeong Su Kim2, Suk-Won Song2
1Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Republic of Korea.
2Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
3Department of Mechanical and Biomedical Engineering, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Republic of Korea
Purpose : The aim of this analysis is to evaluated impact of dual cannulation on the visceral perfusion during aortic dissection repair.
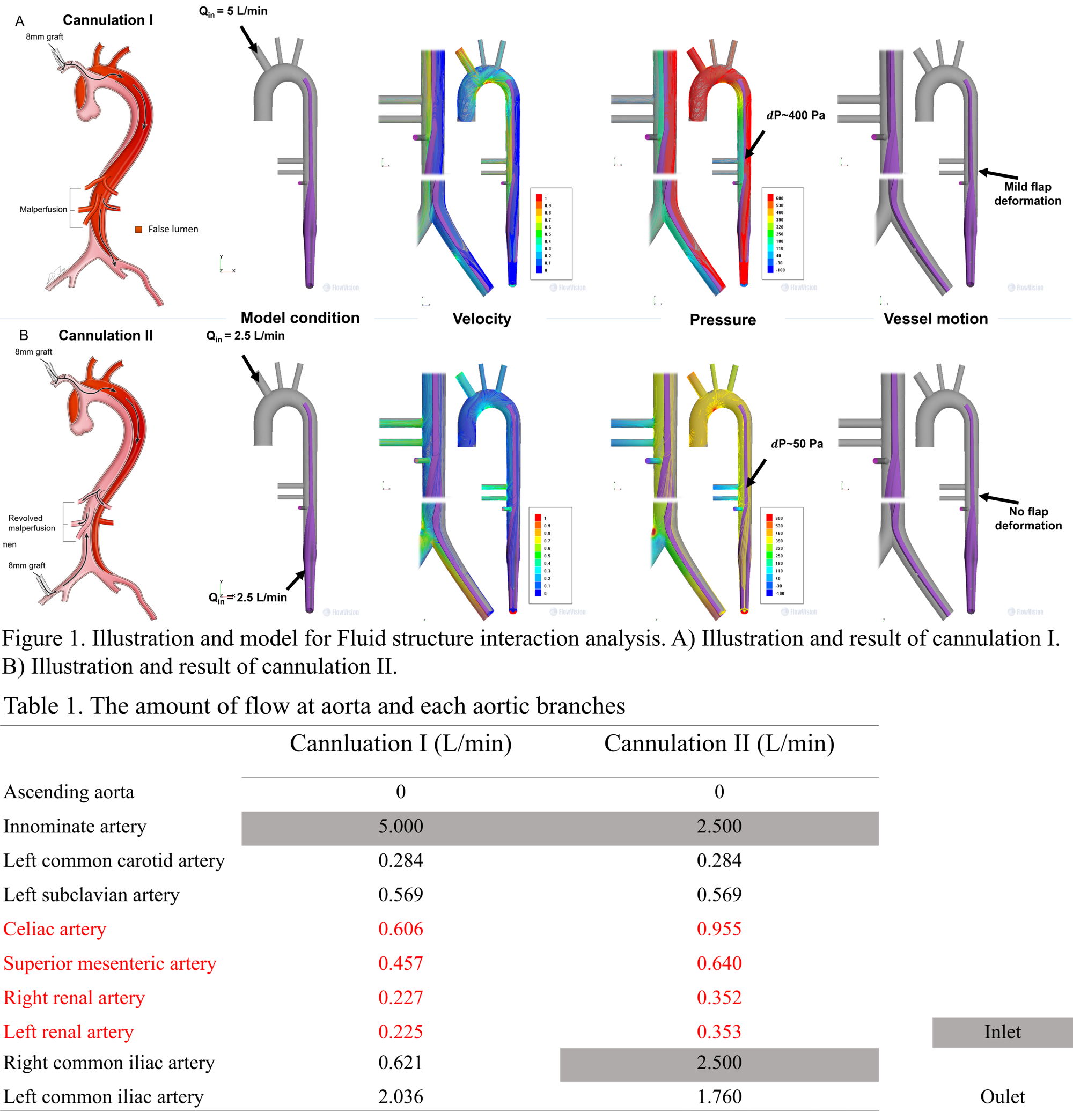
Methods : The model was made assuming the visceral malperfusion in aortic dissection. Two cases of Fluid-structural interaction analysis were conducted with this model. The first case has innominate artery (IA) cannulation (cannulation I), and the second case has dual (IA and femoral) cannulation (cannulation II). In analysis, the the inlet conditions were given to IA at 5L/min for the cannulation I, and the IA and femoral artery at 2.5L/min each for the cannulation II
Results : In cannulation I, false lumen pressure was increased because of the intimal flap motion. The difference of pressure between true and false lumen (∆P) at celiac artery level was 400 Pa. and, the amount of visceral flow (celiac, superior mesenteric, right renal and left renal artery) were 0.606, 0.457, 0.227 and 0.225 L/min, respectively. However, in cannulation II, ∆P at celiac artery level was decreased to 50 Pa. and, the amount of visceral flow was increased at all branches (0.955, 0.640, 0.352 and 0.353 L/min, respectively) (Table 1) (Figure 1).
Conclusion : We confirmed dual cannulation increase visceral flow by decrease the pressure difference between true and false lumen by Fluid-structural interaction analysis. If we add retrograde flow from the femoral cannulation, visceral malperfusion may be resolved.
Methods : The model was made assuming the visceral malperfusion in aortic dissection. Two cases of Fluid-structural interaction analysis were conducted with this model. The first case has innominate artery (IA) cannulation (cannulation I), and the second case has dual (IA and femoral) cannulation (cannulation II). In analysis, the the inlet conditions were given to IA at 5L/min for the cannulation I, and the IA and femoral artery at 2.5L/min each for the cannulation II
Results : In cannulation I, false lumen pressure was increased because of the intimal flap motion. The difference of pressure between true and false lumen (∆P) at celiac artery level was 400 Pa. and, the amount of visceral flow (celiac, superior mesenteric, right renal and left renal artery) were 0.606, 0.457, 0.227 and 0.225 L/min, respectively. However, in cannulation II, ∆P at celiac artery level was decreased to 50 Pa. and, the amount of visceral flow was increased at all branches (0.955, 0.640, 0.352 and 0.353 L/min, respectively) (Table 1) (Figure 1).
Conclusion : We confirmed dual cannulation increase visceral flow by decrease the pressure difference between true and false lumen by Fluid-structural interaction analysis. If we add retrograde flow from the femoral cannulation, visceral malperfusion may be resolved.
책임저자: Suk-Won Song
Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
발표자: Woon Heo, E-mail : woonheo83@gmail.com


