초록접수 현황
| 20F-008 | 구연 발표 |
Clinical Utility of Tumor Regression Grade Combined with Lymph Node Status in Patients with Advanced Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Jae Kwang Yun1, Youngwoong Kim2, Geun Dong Lee1, Sehoon Choi1, Yong-Hee Kim1, Dong Kwan Kim1, Seung-Il Park1, and Hyeong Ryul Kim1.
1 Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
2 Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Republic of Korea
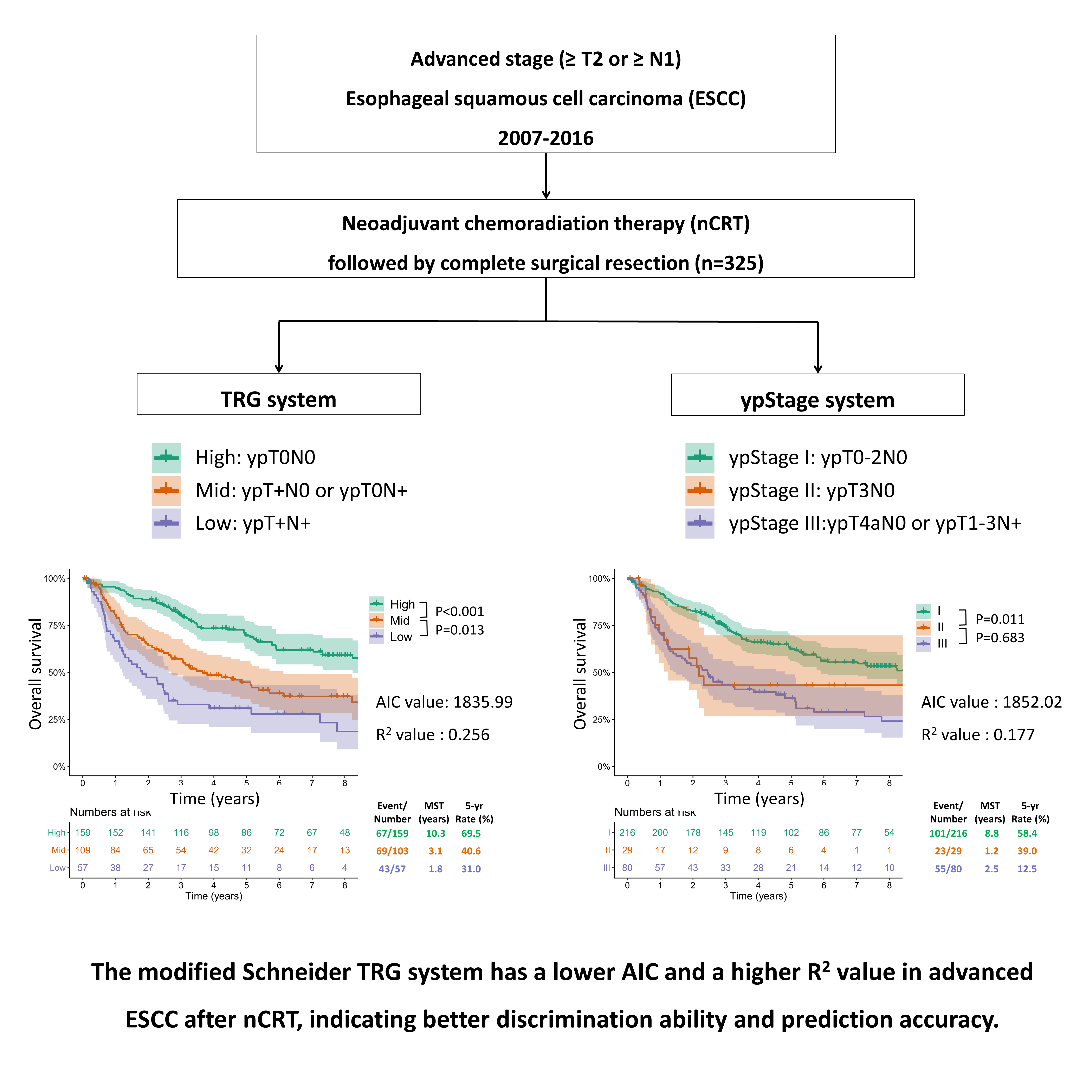
Purpose : This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of tumor regression grade (TRG) combined with lymph node status compared with the 8th edition of the ypTNM staging system in patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell cancer (EC) after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT).
Methods : We enrolled 325 patients with EC who underwent nCRT followed by complete resection. We adopted the modified Schneider TRG system, with high (ypT0N0), mid (ypT0N+ or ypT+N0), and low (ypT+N+). After developing a multivariable Cox model, the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) and R2 measure were used to evaluate the discrimination ability of the ypStage and TRG systems.
Results : The mean duration of follow-up was 56.7 ± 43.3 months. The survival curves between the adjacent groups of TRG were significantly different for both overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS). However, there were no significant differences between ypStages II and III for OS (p = 0.683) or RFS (p = 0.760). The TRG system also had a discrimination ability in patients with ypStage I (p < 0.001 for both OS and RFS) and ypStage III (p = 0.045 for OS and 0.042 for RFS). Compared with the ypTNM staging system, the modified TRG had a lower AIC value (1835.99 vs. 1852.02) and a higher R2 (0.256 vs. 0.177), indicating better discrimination ability and prediction accuracy.
Conclusion : For patients with EC who underwent esophagectomy following nCRT, the modified Schneider TRG system may complement the ypStage and help clinicians select the most appropriate postoperative treatment and surveillance.
Methods : We enrolled 325 patients with EC who underwent nCRT followed by complete resection. We adopted the modified Schneider TRG system, with high (ypT0N0), mid (ypT0N+ or ypT+N0), and low (ypT+N+). After developing a multivariable Cox model, the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) and R2 measure were used to evaluate the discrimination ability of the ypStage and TRG systems.
Results : The mean duration of follow-up was 56.7 ± 43.3 months. The survival curves between the adjacent groups of TRG were significantly different for both overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS). However, there were no significant differences between ypStages II and III for OS (p = 0.683) or RFS (p = 0.760). The TRG system also had a discrimination ability in patients with ypStage I (p < 0.001 for both OS and RFS) and ypStage III (p = 0.045 for OS and 0.042 for RFS). Compared with the ypTNM staging system, the modified TRG had a lower AIC value (1835.99 vs. 1852.02) and a higher R2 (0.256 vs. 0.177), indicating better discrimination ability and prediction accuracy.
Conclusion : For patients with EC who underwent esophagectomy following nCRT, the modified Schneider TRG system may complement the ypStage and help clinicians select the most appropriate postoperative treatment and surveillance.
책임저자: Hyeong Ryul Kim
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Asan Medical Center, Ulsan University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
발표자: Hyeong Ryul Kim, E-mail : janies@nate.com


