초록접수 현황
| 19F-179 | 구연 미채택시 포럼 발표 |
Survival outcome and prognostic factors after postoperative recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer
Yoohwa hwang, Wan Jin Hwang, Soyoung Lee, Mincheol Chae, Woohyun Jung, Jae Hyun Jeon, Sukki Cho, Kwhanmien Kim, Sanghoon Jheon
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Purpose : Since survival after postoperative non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) recurrence is extremely poor, the long term post recurrence outcomes are not well understood. The purpose of this study was to evaluate long-term post-recurrence outcomes and clarify the prognostic factor of postoperative-recurrence of NSCLC.
Methods : From 3501 patients with R0 resected pathologic stage IA-IIIC NSCLC between 2003 and 2017, a total of 688 patients who developed recurrence were included in this study. Secondary primary lung cancers and suspected lesions were excluded. Oligo-recurrence was defined as 1-3 loco-regional or distant recurrent lesions restricted to a single organ. Factors associated with post-recurrence survival and the characteristics of the long-term survivors were analyzed retrospectively.
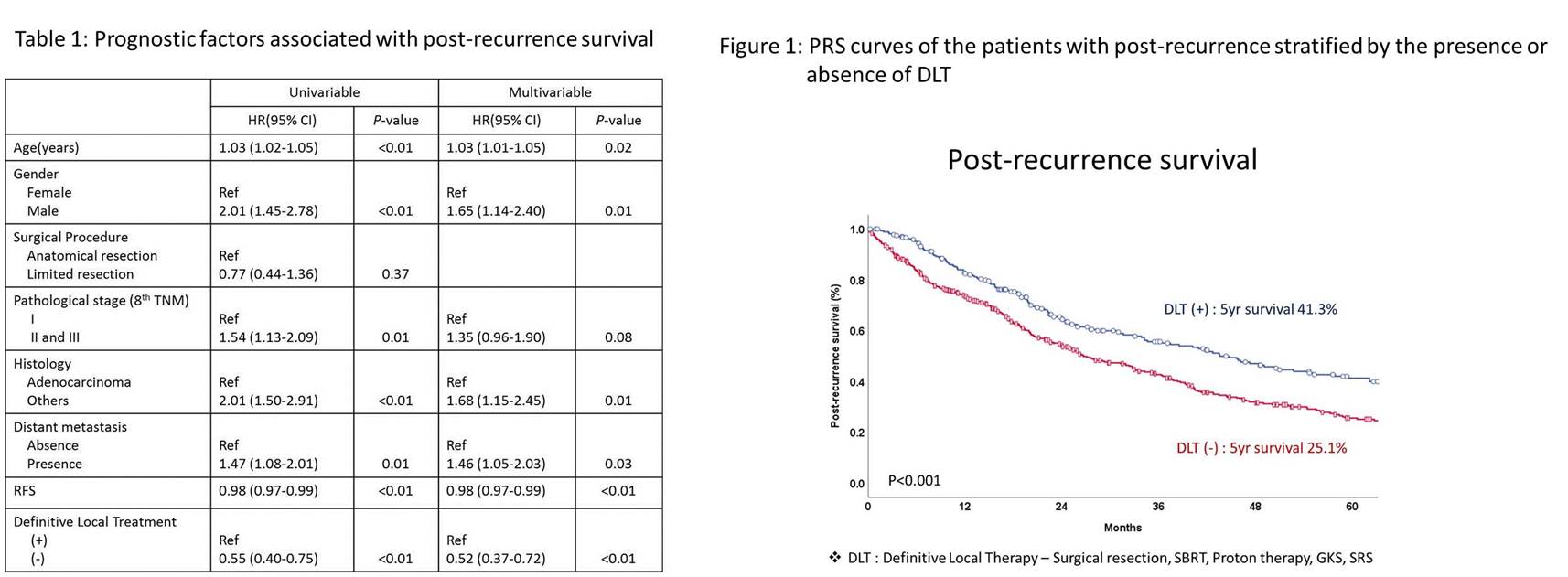
Results : Oligo-recurrence was identified in 377 (54.8%). The 3-year and 5-year post-recurrence survival (PRS) rate of all 688 patients was 47.4% and 31.4%, respectively. Multivariable analysis revealed that younger age, female, adenocarcinoma, loco-regional recurrence, initial definitive local treatment (DLT) and longer recurrence free survival were significant prognostic factors for PRS. (Table 1) The initial pathological stage did not affect PRS. DLT was performed in 269 (39.1%) as initial treatment in total postoperative recurrence and was conducted frequently for oligo-recurrence in the lung, regional lymph nodes and brain. The 5-PRS were significantly higher in DLT group (41.3% vs 25.1%, p<0.001) (Figure 1).
Conclusion : Initial definitive local treatment including surgical resection or definitive ratiotherapy for postoperative non-small cell lung cancer recurrence achieved favorable long term post-recurrence survival in a selected population.
Methods : From 3501 patients with R0 resected pathologic stage IA-IIIC NSCLC between 2003 and 2017, a total of 688 patients who developed recurrence were included in this study. Secondary primary lung cancers and suspected lesions were excluded. Oligo-recurrence was defined as 1-3 loco-regional or distant recurrent lesions restricted to a single organ. Factors associated with post-recurrence survival and the characteristics of the long-term survivors were analyzed retrospectively.
Results : Oligo-recurrence was identified in 377 (54.8%). The 3-year and 5-year post-recurrence survival (PRS) rate of all 688 patients was 47.4% and 31.4%, respectively. Multivariable analysis revealed that younger age, female, adenocarcinoma, loco-regional recurrence, initial definitive local treatment (DLT) and longer recurrence free survival were significant prognostic factors for PRS. (Table 1) The initial pathological stage did not affect PRS. DLT was performed in 269 (39.1%) as initial treatment in total postoperative recurrence and was conducted frequently for oligo-recurrence in the lung, regional lymph nodes and brain. The 5-PRS were significantly higher in DLT group (41.3% vs 25.1%, p<0.001) (Figure 1).
Conclusion : Initial definitive local treatment including surgical resection or definitive ratiotherapy for postoperative non-small cell lung cancer recurrence achieved favorable long term post-recurrence survival in a selected population.
책임저자: Kwhanmien Kim
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
발표자: Yoohwa Hwang, E-mail : yooflower@snubh.org








