초록접수 현황
| 19F-159 | 구연 발표 |
Injury Severity Scoring Systems as a Predictor of Renal Replacement Therapy in Chest Trauma
Do Wan Kim, Kyo Seon Lee, Sang Gi Oh, Yo Chun Jung, Kook Joo Na, Sang Yun Song, In Seok Jeong
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Republic of Korea
Purpose : Injury Severity Scoring Systems(ISSS) are widely used for evaluation of severe trauma patients. And, the effectiveness of renal replacement therapy(RRT) for patients with acute kidney injury is well-established.However, there were no sufficient studies of correlation between ISSS and RRT on chest trauma. We evaluated the efficacy of ISSS prediction the application of RRT in chest trauma patients.
Methods : We retrospectively analyzed patients who admitted to regional trauma center from January 2014 to May 2019. We excluded patients under 18 years of age, and patients who died within 1 hour of hospital arrival. A total of 11,118 patients visited our trauma center. Of these, a total of 2108 patients with chest trauma were available for analysis. Of these, 70 patients received RRT after admission. We compared the results of trauma scoring system in these patients, including Injury Severity Score(ISS), Revised Trauma Score(RTS), GCS, Trauma Injury Severity Score (TRISS) and shock index (SI).
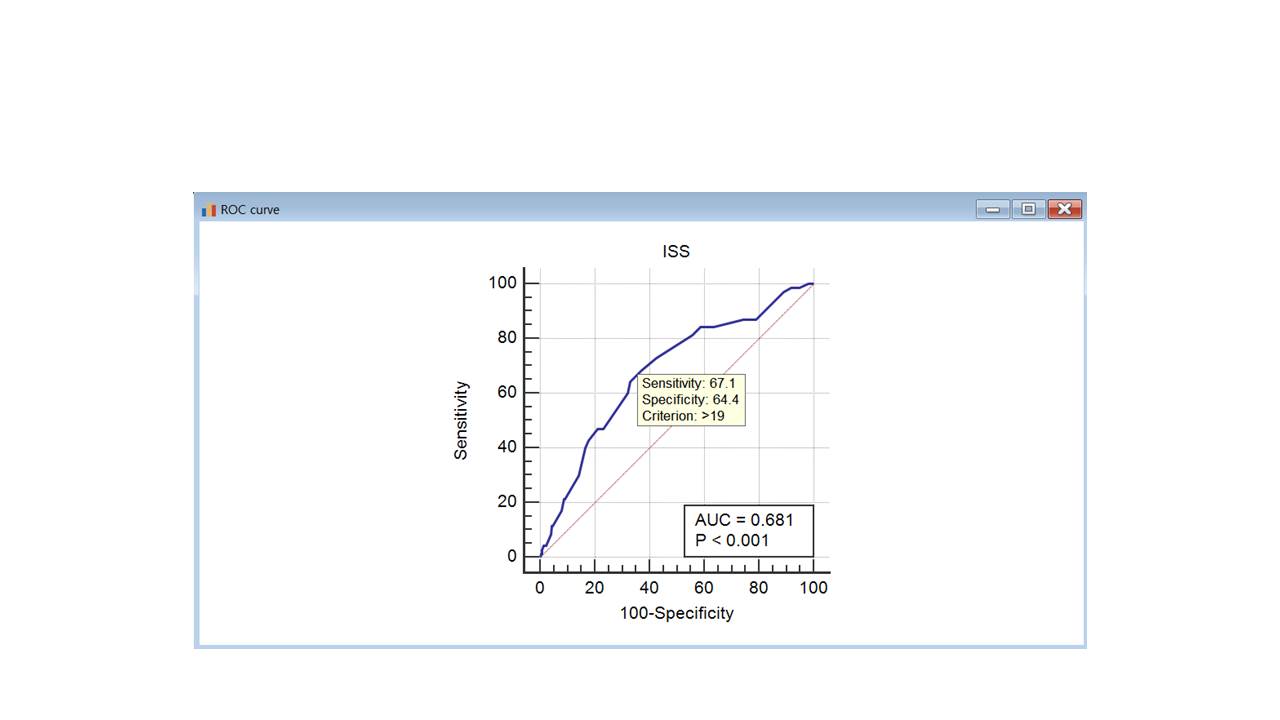
Results : The overall survival rate was 88.3%. The RRT group had a lower survival rate, compared to Non-RRT group (52.8%,P< 0.0001) but duration and initiation timing of RRT were no statistical significance to survival rate (p=0.1594,p=0.3774). The optimal cut-off value of GCS, ISS, TRISS and SI for survival prediction was 13(AUC0.593,p=0.003), 19(AUC0.681,p<0.001), 92.2(AUC0.686,p<0.001) and 0.885(AUC 0.610,p=0.004), respectively. ISS was the only significant scoring system that predict the application of RRT (cut-off value 19,p=0.0004) in patients.
Conclusion : Accurate anticipation of RRT in chest trauma is too difficult to predict using trauma scoring system. However, high ISS was significantly associated with start of RRT.
Methods : We retrospectively analyzed patients who admitted to regional trauma center from January 2014 to May 2019. We excluded patients under 18 years of age, and patients who died within 1 hour of hospital arrival. A total of 11,118 patients visited our trauma center. Of these, a total of 2108 patients with chest trauma were available for analysis. Of these, 70 patients received RRT after admission. We compared the results of trauma scoring system in these patients, including Injury Severity Score(ISS), Revised Trauma Score(RTS), GCS, Trauma Injury Severity Score (TRISS) and shock index (SI).
Results : The overall survival rate was 88.3%. The RRT group had a lower survival rate, compared to Non-RRT group (52.8%,P< 0.0001) but duration and initiation timing of RRT were no statistical significance to survival rate (p=0.1594,p=0.3774). The optimal cut-off value of GCS, ISS, TRISS and SI for survival prediction was 13(AUC0.593,p=0.003), 19(AUC0.681,p<0.001), 92.2(AUC0.686,p<0.001) and 0.885(AUC 0.610,p=0.004), respectively. ISS was the only significant scoring system that predict the application of RRT (cut-off value 19,p=0.0004) in patients.
Conclusion : Accurate anticipation of RRT in chest trauma is too difficult to predict using trauma scoring system. However, high ISS was significantly associated with start of RRT.
책임저자: Do Wan Kim
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Republic of Korea
발표자: Do Wan Kim, E-mail : maskjoa@naver.com








