초록접수 현황
| 19F-053 | 포스터 발표 |
Total arch Replacement after Failed TEVAR in Ruptured Traumatic Aortic Dissection
Su Young Yoon, Si-Wook Kim, Do-hoon Kim, Jong-Myeon Hong
Trauma Center, Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Chungcheongbuk-do, Republic of Korea
Purpose : Background: Thoracic endovascular aortic replacement (TEVAR) has emerged as an alternative to open repair in traumatic thoracic aortic injuries. But TEVAR could still make quite catastrophic complications in traumatic aortic dissection management including endovascular leaks.
Methods : We experienced a case of successful arch replacement of aortic rupture due to wire protrusion of proximal landing zone and catastrophic bleeding after TEVAR.
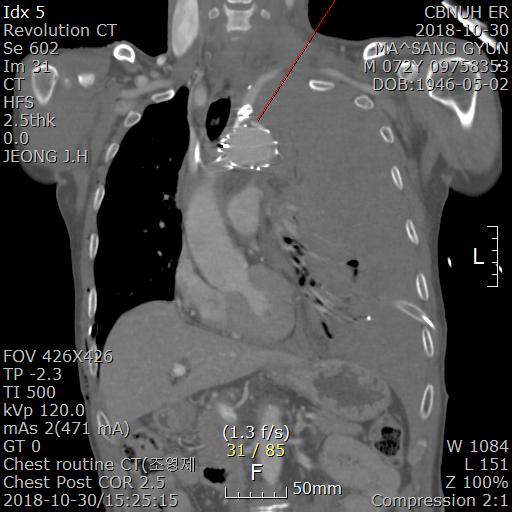
Results : Case report: A 72-year-old male patient was transferred to our trauma center by a helicopter due to massive car accident. The patient complained of severe back pain with multiple trauma, and chest computed tomography (CT) showed aortic rupture at proximal descending thoracic aorta with large hemomediastinum and hemothorax at left thoracic cavity. Abdominal CT showed retroperitoneal hematoma with dislocation of hip joint. Emergent TEVAR (Valiant 38 x 38 x 200mm) with proximal landing at zone 2 with left subclavian artery embolization was performed by an intervention cardiologist. After TEVAR, continuous large amount of bleeding was drained via left chest tube to 1700 ml, and systolic blood pressure was dropping to 50~70 mmHg. Emergent operation was performed thru median sternotomy with femoral approach. Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) was started through femoral artery and vein, and extended thoracotomy thru left 4th intercostal space was added. We found the bleeding site at lesser curvature of aortic arch with wire protrusion of proximal landing zone exposed to the outside of the aorta. With circulatory arrest, total arch replacement were performed using a branched Hemashield (30 mm, Hemashield Platinum) with three-branched arch graft (12x8x8 mm, Hemashield Platinum). Bleeding was still continued around anastomotic sites with prolonged coagulation time and temporary wound closure was performed with gauze packings around the anastomotic areas. After 3 days later, reexploration was done for bleeding control with packed-gauze removal and wound closure was done layer by layer. Even though the patient had to be reoperated with vacuum suction drainage because of the superficial wound infection, he could move to the ward for rehabilitation at postoperative 82 days with full recovery of consciousness and motor functions
Conclusion : Conclusions: In a traumatic aortic rupture, TEVAR has been a primary choice of management rather than open thoracotomy. But TEVAR has still complications of leakages and fracture failure, especially at aortic arch portion. We report a case of successful arch replacement of aortic rupture because of wire protrusion of proximal landing zone of TEVAR which was done due to traumatic aortic rupture.
Methods : We experienced a case of successful arch replacement of aortic rupture due to wire protrusion of proximal landing zone and catastrophic bleeding after TEVAR.
Results : Case report: A 72-year-old male patient was transferred to our trauma center by a helicopter due to massive car accident. The patient complained of severe back pain with multiple trauma, and chest computed tomography (CT) showed aortic rupture at proximal descending thoracic aorta with large hemomediastinum and hemothorax at left thoracic cavity. Abdominal CT showed retroperitoneal hematoma with dislocation of hip joint. Emergent TEVAR (Valiant 38 x 38 x 200mm) with proximal landing at zone 2 with left subclavian artery embolization was performed by an intervention cardiologist. After TEVAR, continuous large amount of bleeding was drained via left chest tube to 1700 ml, and systolic blood pressure was dropping to 50~70 mmHg. Emergent operation was performed thru median sternotomy with femoral approach. Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) was started through femoral artery and vein, and extended thoracotomy thru left 4th intercostal space was added. We found the bleeding site at lesser curvature of aortic arch with wire protrusion of proximal landing zone exposed to the outside of the aorta. With circulatory arrest, total arch replacement were performed using a branched Hemashield (30 mm, Hemashield Platinum) with three-branched arch graft (12x8x8 mm, Hemashield Platinum). Bleeding was still continued around anastomotic sites with prolonged coagulation time and temporary wound closure was performed with gauze packings around the anastomotic areas. After 3 days later, reexploration was done for bleeding control with packed-gauze removal and wound closure was done layer by layer. Even though the patient had to be reoperated with vacuum suction drainage because of the superficial wound infection, he could move to the ward for rehabilitation at postoperative 82 days with full recovery of consciousness and motor functions
Conclusion : Conclusions: In a traumatic aortic rupture, TEVAR has been a primary choice of management rather than open thoracotomy. But TEVAR has still complications of leakages and fracture failure, especially at aortic arch portion. We report a case of successful arch replacement of aortic rupture because of wire protrusion of proximal landing zone of TEVAR which was done due to traumatic aortic rupture.
책임저자: Su Young Yoon
Trauma Center, Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Chungcheongbuk-do, Republic of Korea
발표자: Su Young Yoon, E-mail : ysy1227@hanmai.lnet








