초록접수 현황
| 16F-229 | 구연 발표 |
Effect of Undertreatment in Recurrence of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Analysis of Patients Underwent Curative Surgical Resection
Hye-seon Kim, Hyuck Kim, Won Sang Chung
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Hanyang University Medical Center, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Background : Physicians always try treat for their patients with non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC) by the best evidence based therapy. But guideline based treatment is not always applicable to every patient because of various factors. In this study, we tried to analyze the effect of undertreatment in survival of patients with NSCLC who underwent surgical resection.
Methods : From January 2011 to December 2015, 188 patients underwent surgical treatment for NSCLC with curative intention at out center. Eight patients with stage 0 were excluded in this study. We adopted NCCN guidelines Ver 4. 2016 in defining proper treatment. Undertreatment is defined as sublobar resection in unsuitable patients, incomplete mediastinal lymph node dissection and absence of adjuvant therapies in indicated cases. We retrospectively reviewed medical records and classified patients into undertreatment group (UT) (n=44) and proper treatment group (PT) (n=136). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis on cancer recurrence was performed.
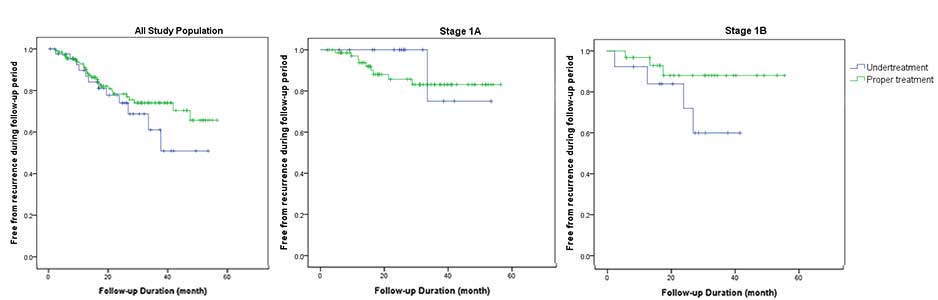
Results : The follow up duration of patients was mean 30.03 months. The survival curve of all study population showed distinctive curve between UT and PT group, though p-values was 0.310. Stage-stratified analysis was performed for stage IA and IB which were suitable to subgroup analysis owing to sufficient cases. The survival curve for both stage IA and IB showed quite different survival curve between UT and PT group. However, p-values by log-rank test were 0.456 and 0.118, respectively for each stage.
Conclusion : PT group showed superior survival curve to UT group, especially in later period (> 3 years) though p-values were insufficient to statistic significance. Though there is limitation in interpretation because of small number of study population, we can conclude that proper treatment based on current clinical guideline is preferred to obtain lower recurrence rate. Limited pulmonary resection, selective lymph node evaluation and exemption of adjuvant treatment should be considered in selective patients with inevitable clinical situation.
Methods : From January 2011 to December 2015, 188 patients underwent surgical treatment for NSCLC with curative intention at out center. Eight patients with stage 0 were excluded in this study. We adopted NCCN guidelines Ver 4. 2016 in defining proper treatment. Undertreatment is defined as sublobar resection in unsuitable patients, incomplete mediastinal lymph node dissection and absence of adjuvant therapies in indicated cases. We retrospectively reviewed medical records and classified patients into undertreatment group (UT) (n=44) and proper treatment group (PT) (n=136). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis on cancer recurrence was performed.
Results : The follow up duration of patients was mean 30.03 months. The survival curve of all study population showed distinctive curve between UT and PT group, though p-values was 0.310. Stage-stratified analysis was performed for stage IA and IB which were suitable to subgroup analysis owing to sufficient cases. The survival curve for both stage IA and IB showed quite different survival curve between UT and PT group. However, p-values by log-rank test were 0.456 and 0.118, respectively for each stage.
Conclusion : PT group showed superior survival curve to UT group, especially in later period (> 3 years) though p-values were insufficient to statistic significance. Though there is limitation in interpretation because of small number of study population, we can conclude that proper treatment based on current clinical guideline is preferred to obtain lower recurrence rate. Limited pulmonary resection, selective lymph node evaluation and exemption of adjuvant treatment should be considered in selective patients with inevitable clinical situation.
책임저자: Hye-seon Kim
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Hanyang University Medical Center, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
발표자: Hye-seon Kim, E-mail : hestiahskim@kei.pe.kr








