초록접수 현황
| 16F-228 | 구연 발표 |
Prognostic Impact of Pathologic Microscopic Lymphovascular Invasion According to Tumor Size in Completely Resected pT1-3N0 NSCLC
:Implication to the T Descriptor
Sumin Shin, Yong Soo Choi, Jong Ho Cho, Hong Kwan Kim, Jhingook Kim, Jae Ill Zo, Young Mog Shim
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Background : The prognostic significance of microscopic lymph vascular invasion(MVI) in non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC) remains controversial. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effect of MVI and tumor size in the recurrence free survival(RFS) for NSCLC and determine the implication of MVI to the T descriptor.
Methods : From 2008 to 2012, a total of 1,473 eligible patients with pathologic T1-3N0 NSCLC who underwent complete resection with systematic lymph node dissection without induction treatment were included the study. The tumor size was categorized as ≤2cm, 2 to 3cm, 3 to 5cm and greater than 5cm. RFS were estimated using Kaplan-Meier methods and the log-rank tests. The Cox proportional hazard model was used to assess independent effect of MVI for RFS.
Results : MVI was observed in 495 patients(33.6%), and MVI (+) group showed significantly worse survival compared to MVI(-) group(estimated 5-year RFS; 54% vs 75.8%, p<0.001). In the multivariable analysis adjusting clinical variables including age, sex, histology, differentiation, visceral pleural invasion and type of surgery, MVI was independent prognostic factor for poorer RFS(adjusted hazard ratio=1.87, p<0.001).
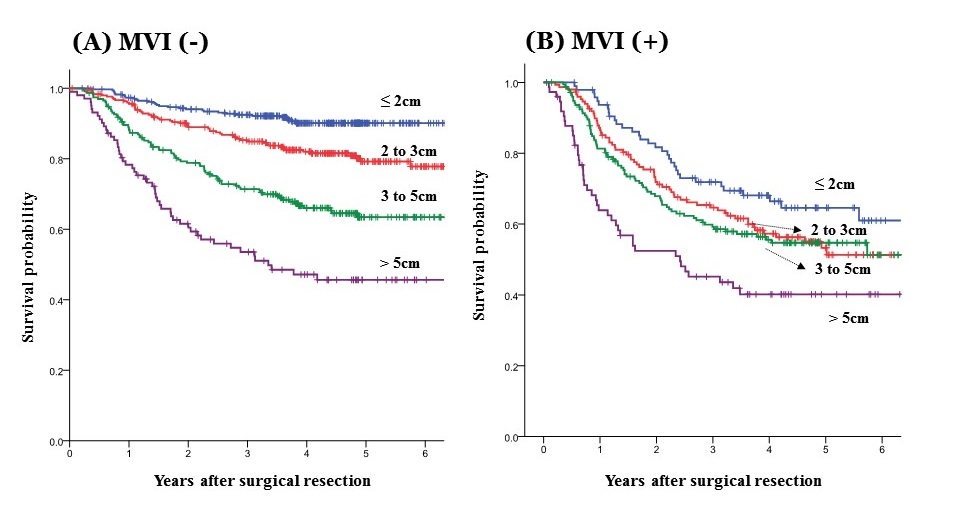
In patients without MVI, RFS decreased in accordance with increasing tumor size (90.1%, 79.2%, 63.4% and 45.6%). Meanwhile, in MVI(+) group, RFS was not gradually associated with tumor size (64.6%, 53.3%, 54.7% and 40.2%). Estimated 5-year RFS of tumors≤3cm with MVI was consistent with tumors sized 3 to 5cm without MVI. Statistical significance of MVI for RFS was not found in patients with tumors greater than 5cm.
Conclusion : This study demonstrated that MVI was a significant prognostic factor for survival in the tumor less than 5cm. MVI could be considered additional T descriptor in the future revision of the TNM system for NSCLC.
Methods : From 2008 to 2012, a total of 1,473 eligible patients with pathologic T1-3N0 NSCLC who underwent complete resection with systematic lymph node dissection without induction treatment were included the study. The tumor size was categorized as ≤2cm, 2 to 3cm, 3 to 5cm and greater than 5cm. RFS were estimated using Kaplan-Meier methods and the log-rank tests. The Cox proportional hazard model was used to assess independent effect of MVI for RFS.
Results : MVI was observed in 495 patients(33.6%), and MVI (+) group showed significantly worse survival compared to MVI(-) group(estimated 5-year RFS; 54% vs 75.8%, p<0.001). In the multivariable analysis adjusting clinical variables including age, sex, histology, differentiation, visceral pleural invasion and type of surgery, MVI was independent prognostic factor for poorer RFS(adjusted hazard ratio=1.87, p<0.001).
In patients without MVI, RFS decreased in accordance with increasing tumor size (90.1%, 79.2%, 63.4% and 45.6%). Meanwhile, in MVI(+) group, RFS was not gradually associated with tumor size (64.6%, 53.3%, 54.7% and 40.2%). Estimated 5-year RFS of tumors≤3cm with MVI was consistent with tumors sized 3 to 5cm without MVI. Statistical significance of MVI for RFS was not found in patients with tumors greater than 5cm.
Conclusion : This study demonstrated that MVI was a significant prognostic factor for survival in the tumor less than 5cm. MVI could be considered additional T descriptor in the future revision of the TNM system for NSCLC.
책임저자: Yong Soo Choi
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
발표자: Sumin Shin, E-mail : essennee@gmail.com








