초록접수 현황
| 16F-062 | 구연 발표 |
Identification of Metastatic Pulmonary Nodule using Intravenous Injection of ICG: A Pilot Study
Kook Nam Han, Hyun Koo Kim, Young Ho Choi
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Background : The aim of this study is to evaluate the role of ICG during fluorescence-guided pulmonary metastasectomy and to optimize the intravenous injection protocol for intraoperative detection of lung nodule.
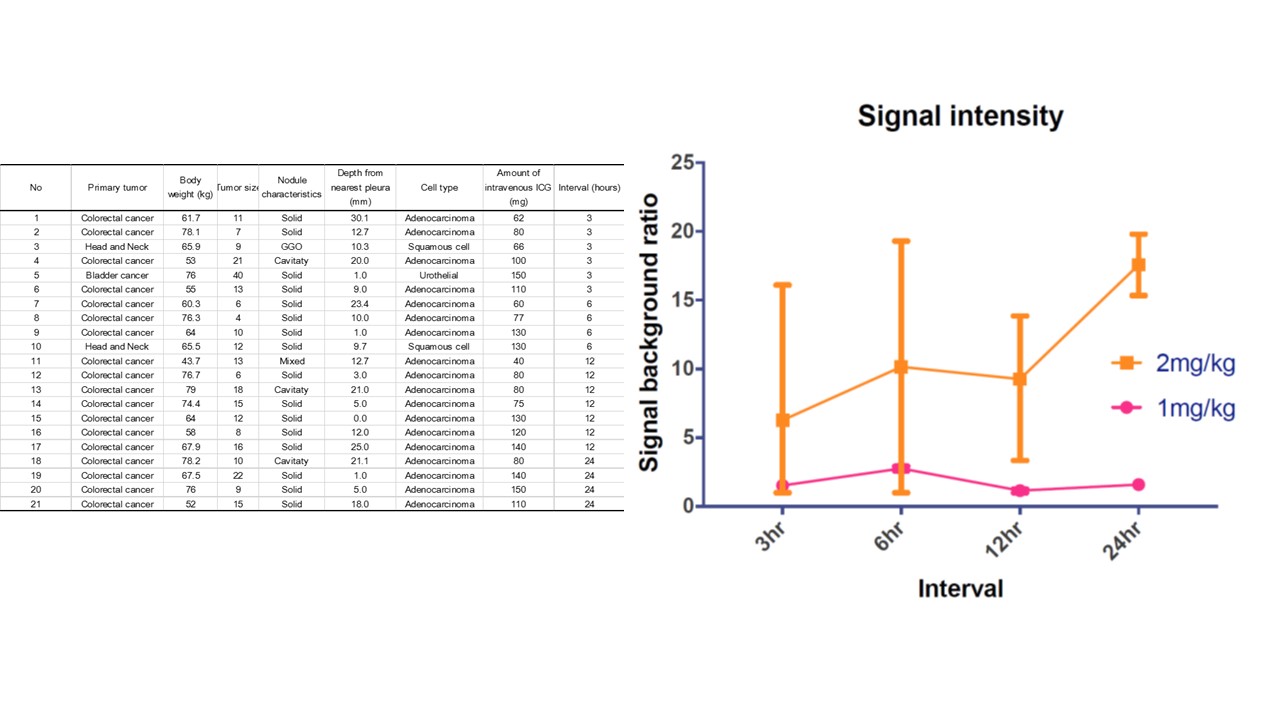
Methods : Twenty-one patients who had planned pulmonary metastasectomy were enrolled in our study. We injected ICG (1 mg/kg in 10 patients; Group I, 2 mg/kg in 11 patients; Group II) intravenously at 3,6,12 and 24 hours before operation. From the resected specimen, we measured fluorescence signal in the operating room using fluorescence camera system and analyzed the signal intensity.
Results : There was no adverse event related with intravenous injection of ICG prior to operation. The size of lung nodules was mean 13±7.8 mm (range: 4-40) Fluorescence signal was detected in 19 nodules (90.4%) and 2 nodules (1 solid and 1 GGO lesion) were not detected on our system. The fluorescence signal intensity increased with ICG dose (1 mg/kg and 2 mg/kg, p<0.001), with peak value of signal to background ratio (SBR) at 6 hour in Group I (2.76±0.22) and 24 hour in Group II (17.58±3.15). In this study, there was no significant relation between cell type or size of nodule, and fluorescence signal intensity.
Conclusion : Intravenous administration of ICG is a feasible method to identify metastatic pulmonary nodule using fluorescence system. Future study is needed to demonstrate the optimal protocol by nodule characteristics in large series.
Methods : Twenty-one patients who had planned pulmonary metastasectomy were enrolled in our study. We injected ICG (1 mg/kg in 10 patients; Group I, 2 mg/kg in 11 patients; Group II) intravenously at 3,6,12 and 24 hours before operation. From the resected specimen, we measured fluorescence signal in the operating room using fluorescence camera system and analyzed the signal intensity.
Results : There was no adverse event related with intravenous injection of ICG prior to operation. The size of lung nodules was mean 13±7.8 mm (range: 4-40) Fluorescence signal was detected in 19 nodules (90.4%) and 2 nodules (1 solid and 1 GGO lesion) were not detected on our system. The fluorescence signal intensity increased with ICG dose (1 mg/kg and 2 mg/kg, p<0.001), with peak value of signal to background ratio (SBR) at 6 hour in Group I (2.76±0.22) and 24 hour in Group II (17.58±3.15). In this study, there was no significant relation between cell type or size of nodule, and fluorescence signal intensity.
Conclusion : Intravenous administration of ICG is a feasible method to identify metastatic pulmonary nodule using fluorescence system. Future study is needed to demonstrate the optimal protocol by nodule characteristics in large series.
책임저자: Hyun Koo Kim
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
발표자: Kook Nam Han, E-mail : hdoc@korea.ac.kr








