초록접수 현황
| 16F-023 | 구연 발표 |
Tonicity-responsive Enhancer-binding Protein Expression Correlated with Tumor Invasiveness and Prognosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Hyun Jin Cho¹, Shinkwang Kang¹, Jae Hyeon Yu¹, ¹Myung Hoon Na, Sang Do Lee², Hyeong Ryul Kim³, Sung Joon Han¹, Hao Jun Cui¹, Roknuggaman¹, Min-Woong Kang¹
¹Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea, ²Department of Physiology, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea, ³Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
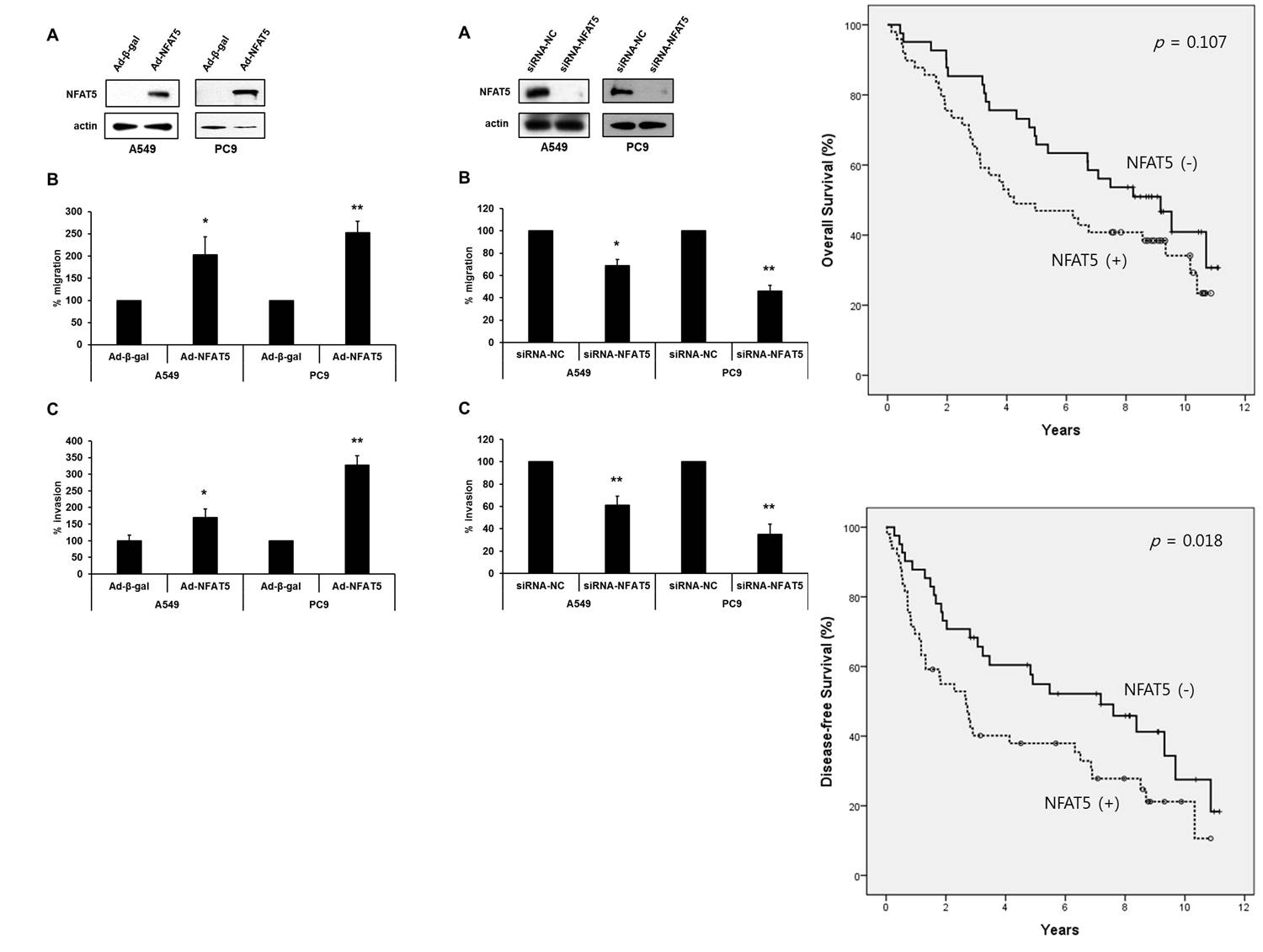
Background : Tonicity-responsive enhancer-binding protein (TonEBP, also known as NFAT5) is a DNA-binding factor to regulate the expression of osmoprotective genes and to play important roles in inflammatory process and cell differentiation. Recent reports have suggested that TonEBP contribute to migration, invasion or metastasis of malignant tumor in vitro. In the present study, we aimed to compare migration/invasion of NSCLC cells according to degree of TonEBP expression and subsequently to compare clinical prognosis according to expression of TonEBP.
Methods : Expression of TonEBP is depressed by small interfering RNA (siRNA) and augmented by adenovirus (Ad) using A549 and PC9 cell lines in vitro. Immunohistochemistry stain of TonEBP is accomplished by tissue microarray from tumor specimens of 90 patients underwent curative surgery for NSCLC at Chungnam National University Hospital between 2004 and 2007.
Results : Migration/invasion of TonEBP-targeting siRNA (siRNA-TonEBP) A549/PC9 cells were significantly decreased than migration/invasion of negative control siRNA (siRNA-NC) A549/PC9 cells (p=0.016 and p<0.01, respectively; p<0.01 and p<0.01, respectively). Migration/invasion of Ad-TonEBP A549/PC9 cells were significantly increased than migration/invasion of Ad-β-gal A549/PC9 cells (p=0.043 and p<0.01, respectively; p<0.048 and p<0.01, respectively). In multivariate analysis, TonEBP (+) and pathologic N1-2 (vs. N0) were significant independent risk factors of recurrence (p=0.025 and p=0.024, respectively). 5-year DFS of TonEBP (-) group and TonEBP (+) group were 54.9±7.9% and 37.9±7.0%, respectively (p=0.018). TonEBP (+), pathologic T3-4 (vs. T1-2) and N1-2 (vs. N0) were significant independent risk factors of DFS (p=0.044, p<0.001, and p=0.016, respectively).
Conclusion : TonEBP expression had shown significant increase of tumor cell migration and invasion from an in vitro study that had used A549 cell line and PC9 cell line. In patients with non-small cell lung cancer, TonEBP expression based on IHC staining of TMA was significantly correlated with the disease recurrence and the patient prognosis, and it was significant independent risk factor of the DFS.
Methods : Expression of TonEBP is depressed by small interfering RNA (siRNA) and augmented by adenovirus (Ad) using A549 and PC9 cell lines in vitro. Immunohistochemistry stain of TonEBP is accomplished by tissue microarray from tumor specimens of 90 patients underwent curative surgery for NSCLC at Chungnam National University Hospital between 2004 and 2007.
Results : Migration/invasion of TonEBP-targeting siRNA (siRNA-TonEBP) A549/PC9 cells were significantly decreased than migration/invasion of negative control siRNA (siRNA-NC) A549/PC9 cells (p=0.016 and p<0.01, respectively; p<0.01 and p<0.01, respectively). Migration/invasion of Ad-TonEBP A549/PC9 cells were significantly increased than migration/invasion of Ad-β-gal A549/PC9 cells (p=0.043 and p<0.01, respectively; p<0.048 and p<0.01, respectively). In multivariate analysis, TonEBP (+) and pathologic N1-2 (vs. N0) were significant independent risk factors of recurrence (p=0.025 and p=0.024, respectively). 5-year DFS of TonEBP (-) group and TonEBP (+) group were 54.9±7.9% and 37.9±7.0%, respectively (p=0.018). TonEBP (+), pathologic T3-4 (vs. T1-2) and N1-2 (vs. N0) were significant independent risk factors of DFS (p=0.044, p<0.001, and p=0.016, respectively).
Conclusion : TonEBP expression had shown significant increase of tumor cell migration and invasion from an in vitro study that had used A549 cell line and PC9 cell line. In patients with non-small cell lung cancer, TonEBP expression based on IHC staining of TMA was significantly correlated with the disease recurrence and the patient prognosis, and it was significant independent risk factor of the DFS.
책임저자: Min-Woong Kang
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
발표자: Hyun Jin Cho, E-mail : irainy79@naver.com








