초록접수 현황
| 15F-214 | 구연 발표 |
Factors Associated with Rapid Progression of Right Ventricular Enlargement after Repair of Tetralogy of Fallot Based on Serial Magnetic Resonance Imaging
신유림, 박영환, 신홍주, 박한기
연세대학교 의과대학 세브란스병원 흉부외과학교실
Background : Although progressive right ventricular enlargement (RVE) is common in patients with pulmonary regurgitation (PR) after tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) repair, rate of RVE varies among the patients. The aim of this study is to investigate independent predictors for rapid RVE based on serial cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Methods : Consecutive patients who had serial cardiac MRIs more than twice between January 2005 and March 2015 after repair of TOF were included in this study. Patients who underwent surgical pulmonary valve implantation or any trans-catheter cardiac intervention between two consecutive MRI studies were excluded from the study. Included patients were divided into two groups by the rate of RVE. The upper first quartile of the patients was considered to have rapid right ventricular dilation (defined as rapid RVE group). Remaining patients in other three quartiles consisted non-rapid RVE group. Group comparisons and multiple logistic regression analysis were performed to identify independent risk factors for rapid RVE.
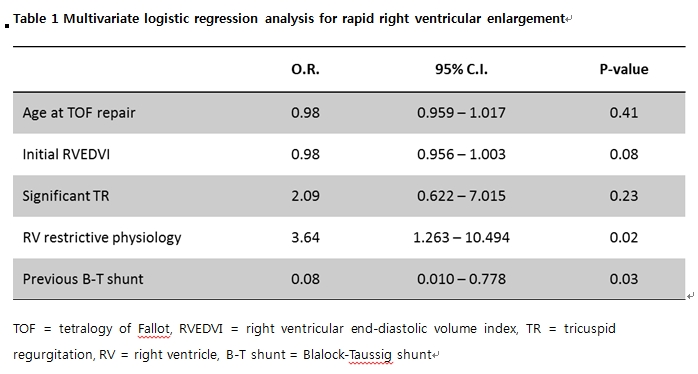
Results : A total of 116 patients were included in the study. Mean number of cardiac MRI performed per patient was 2.8 ± 0.8. Time to initial MRI after TOF repair and interval between the first and the last MRI was 14.2 ± 10.3 years and 4.5 ± 2.2 years, respectively. Mean right ventricular end-diastolic volume index (RVEDVi) change rate was 2.7 ± 6.1 ml/m2/year. RVEDVi change rate of 4.8 ml/m2/year was a cut-off value between two groups. Initial RVEDVi was not different between two groups. Right ventricular restrictive physiology was an independent risk factor for rapid RVE (Odds ratio, 3.64; 95% confidence interval, 1.263-10.494; p-value = 0.02). A history of previous palliative shunt was a negative predictor for rapid RV dilation (Odds ratio, 0.08; 95% confidence interval, 0.010-0.778; p-value = 0.03, Table 1). Initial RVEDVi, PR fraction, residual pulmonary stenosis, and right ventricular ejection fraction was not associated with rapid RVE.
Conclusion : In patients with PR after TOF repair, right ventricular restrictive physiology is associated with more rapid right ventricular dilation. Therefore, watchful follow-up may be needed in this patient population, and earlier PVR should be considered.
Methods : Consecutive patients who had serial cardiac MRIs more than twice between January 2005 and March 2015 after repair of TOF were included in this study. Patients who underwent surgical pulmonary valve implantation or any trans-catheter cardiac intervention between two consecutive MRI studies were excluded from the study. Included patients were divided into two groups by the rate of RVE. The upper first quartile of the patients was considered to have rapid right ventricular dilation (defined as rapid RVE group). Remaining patients in other three quartiles consisted non-rapid RVE group. Group comparisons and multiple logistic regression analysis were performed to identify independent risk factors for rapid RVE.
Results : A total of 116 patients were included in the study. Mean number of cardiac MRI performed per patient was 2.8 ± 0.8. Time to initial MRI after TOF repair and interval between the first and the last MRI was 14.2 ± 10.3 years and 4.5 ± 2.2 years, respectively. Mean right ventricular end-diastolic volume index (RVEDVi) change rate was 2.7 ± 6.1 ml/m2/year. RVEDVi change rate of 4.8 ml/m2/year was a cut-off value between two groups. Initial RVEDVi was not different between two groups. Right ventricular restrictive physiology was an independent risk factor for rapid RVE (Odds ratio, 3.64; 95% confidence interval, 1.263-10.494; p-value = 0.02). A history of previous palliative shunt was a negative predictor for rapid RV dilation (Odds ratio, 0.08; 95% confidence interval, 0.010-0.778; p-value = 0.03, Table 1). Initial RVEDVi, PR fraction, residual pulmonary stenosis, and right ventricular ejection fraction was not associated with rapid RVE.
Conclusion : In patients with PR after TOF repair, right ventricular restrictive physiology is associated with more rapid right ventricular dilation. Therefore, watchful follow-up may be needed in this patient population, and earlier PVR should be considered.
책임저자: 박한기
연세대학교 의과대학 세브란스병원 흉부외과학교실
연락처 : 신유림, Tel: 02-2228-8480 , E-mail : yull0629@yuhs.ac