초록접수 현황
| 15F-164 | 구연 발표 |
Animal Study for the Cardioprotective Effect of MG-132, a Proteasome Inhibitor, on Doxorubicin-induced Cardiomyopathy and Pressure-overload Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
조원민¹,², 김인섭¹, 민두재³, 조현득⁴
고려대학교 의과대학 대학원 의학과 흉부외과학교실¹, 고려대학교 의과대학 안산병원 흉부외과학교실², 고려대학교 의과대학 안산병원 마취과학교실³, 순천향대학교 의과대학 천안병원 병리학교실⁴
Background : Pathologic stimulus to the myocardium induce pathologic hypertrophy or heart failure. In general, ubiquitin/proteasome system (UPS) is an important pathway of proteolysis in pathologic hypertrophic cardiomyocyte. Therefore, we hypothesize that the Mg-132, proteasome inhibitor might be prevent the hypertrophy of myocardial cells by blocking the UPS pathway. And also it could be showed the different mechanism between the hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy. In addition, NF-kB activation had been observed in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and failing heart. And Androgen receptor (AR) was known as a mediator of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Our study was designed to reveal the cardioprotective effect of Mg-132 for the different cardiomyopathy models by pathophysiologic study and analysis of above mentioned protein.
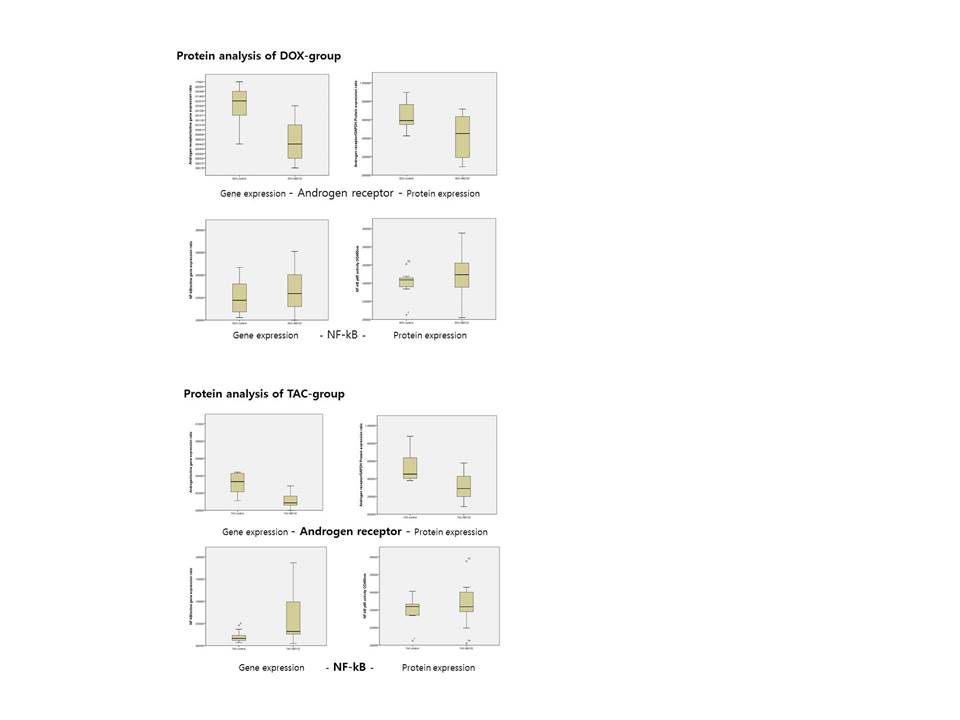
Methods : We constructed two different animal models with Sprague-Dawley rats: ascending aorta constriction induced hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (TAC group) and Doxorubicin administered dilated cardiomyopathy (DOX group) rat model. Each group had three subgroups: ① sham (n=10), ② control (Control-Subgroup; n=10), ③ MG-132 administration (Mg-Subgroup; n=10). During 4 weeks after TAC and DOX model construction, MG-132(0.1mg/Kg/day) was injected subcutaneously. The hemodynamic data and pathologic evaluation were conducted in all animal groups sequentially. After then, the level of AR and NF-kB were measured from left ventricle tissues by real time PCR, ELISA and Western-blot studies for protein analysis.
Results : The hemodynamic data and histologic studies proved that each animal model was suitable to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and dilated cardiomyopathy. Ventricular dP/dT was significantly increased in TAC Mg-subgroup compare to TAC control-subgroup (p=0.03), but not significant in DOX subgroups (p =0.73). Fibrosis was more prevalent in TAC model. Although it was decreased in Mg-subgroup, that was not significant statistically. Mg-subgroups for each TAC and DOX group revealed decreased AR compare to control subgroup for TAC (p=0.04) and DOX group (p=0.02). Although the NF-kB was increased in Mg-subgroup of TAC and DOX compare to control subgroup, it did not show the statistical significance.
Conclusion : Mg-132 suppress AR via blocking UPS in both cardiomyopathy model. Especially, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy showed more prominent reduction of fibrosis with AR blocking. However, NF-kB that is ubiquitous transcription factor might be not related to UPS in this study. From our data, we could hypothesize: 1) Mg-132, proteasome inhibitor might be prevent the hypertrophy of myocardial cells by blocking the UPS pathway inducing fibrosis. 2) MG-132 act on (suppress) AR but not NF-kB. 3) Proteasome inhibitor plays a different role between hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and dilated cardiomyopathy.
Methods : We constructed two different animal models with Sprague-Dawley rats: ascending aorta constriction induced hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (TAC group) and Doxorubicin administered dilated cardiomyopathy (DOX group) rat model. Each group had three subgroups: ① sham (n=10), ② control (Control-Subgroup; n=10), ③ MG-132 administration (Mg-Subgroup; n=10). During 4 weeks after TAC and DOX model construction, MG-132(0.1mg/Kg/day) was injected subcutaneously. The hemodynamic data and pathologic evaluation were conducted in all animal groups sequentially. After then, the level of AR and NF-kB were measured from left ventricle tissues by real time PCR, ELISA and Western-blot studies for protein analysis.
Results : The hemodynamic data and histologic studies proved that each animal model was suitable to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and dilated cardiomyopathy. Ventricular dP/dT was significantly increased in TAC Mg-subgroup compare to TAC control-subgroup (p=0.03), but not significant in DOX subgroups (p =0.73). Fibrosis was more prevalent in TAC model. Although it was decreased in Mg-subgroup, that was not significant statistically. Mg-subgroups for each TAC and DOX group revealed decreased AR compare to control subgroup for TAC (p=0.04) and DOX group (p=0.02). Although the NF-kB was increased in Mg-subgroup of TAC and DOX compare to control subgroup, it did not show the statistical significance.
Conclusion : Mg-132 suppress AR via blocking UPS in both cardiomyopathy model. Especially, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy showed more prominent reduction of fibrosis with AR blocking. However, NF-kB that is ubiquitous transcription factor might be not related to UPS in this study. From our data, we could hypothesize: 1) Mg-132, proteasome inhibitor might be prevent the hypertrophy of myocardial cells by blocking the UPS pathway inducing fibrosis. 2) MG-132 act on (suppress) AR but not NF-kB. 3) Proteasome inhibitor plays a different role between hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and dilated cardiomyopathy.
책임저자: 조원민
고려대학교 의과대학 안산병원 흉부외과학교실
연락처 : 조원민, Tel: 010-9394-7292 , E-mail : jowonmin@gmail.com