초록접수 현황
| 15F-087 | 구연 발표 |
C-reactive Protein Deposition in Myocardiocyte Induces IL-6 Overexpression in Rat Model of Ischemia Reperfusion Injury
오세진¹, 최재성¹, 문현종¹, 성용원¹, 이정상¹, 김은나², 김종재²
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul Municipal Boramae Hospital, Seoul National University Colleage of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea¹, 2Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea²
Background : C-reactive protein (CRP) is an acute phase reactant that is synthesized in the liver and released into the circulation. It has been known that the concentration of CRP in the blood would be a poor prognostic factor in various cardiovascular disease including myocardial infarction. CRP circulates as a pentamer of 5 identical, non-covalently linked subunits in plasma (pCRP). On the damaged cell, however, pCRP has a conformational change to monomeric form (mCRP) and has a potent proinflammatory role. Recent studies showed that mCRP deposition in inflammatory tissues including burn wound and atherosclerotic carotic artery could activate IL-6 and induce the classical complement pathway. We investigated the proinflammatory role of CRP deposition in rat myocardium as a tissue bound form (mCRP) in the ischemia reperfusion injury model.
Methods : Female Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 250g to 300g were used for in vivo study. Myocardial ischemia was produced by ligation of LAD followed by reperfusion. Because CRP in rat does not activate complement system, we infused 200ug of human CRP (pCRP, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) intravenously at the time of reperfusion. Study groups were (1) sham operation (n=2), (2) ischemia-reperfusion injury without human CRP infusion (I/R, n=1), (3) I/R injury (25minutes of ischemia) with human CRP infusion (I/R-CRP, n=1), and (4) I/R injury (45minutes of ischemia) with human CRP infusion (I/R-CRP, n=1). Immunohistochemistry was conducted with a rabbit polyclonal anti-CRP antibody (1:250 dilution, AbCam,Cambridge, UK). Quantitative RT-PCR was used to determine CRP mRNA and IL-6 mRNA levels in heart and liver.
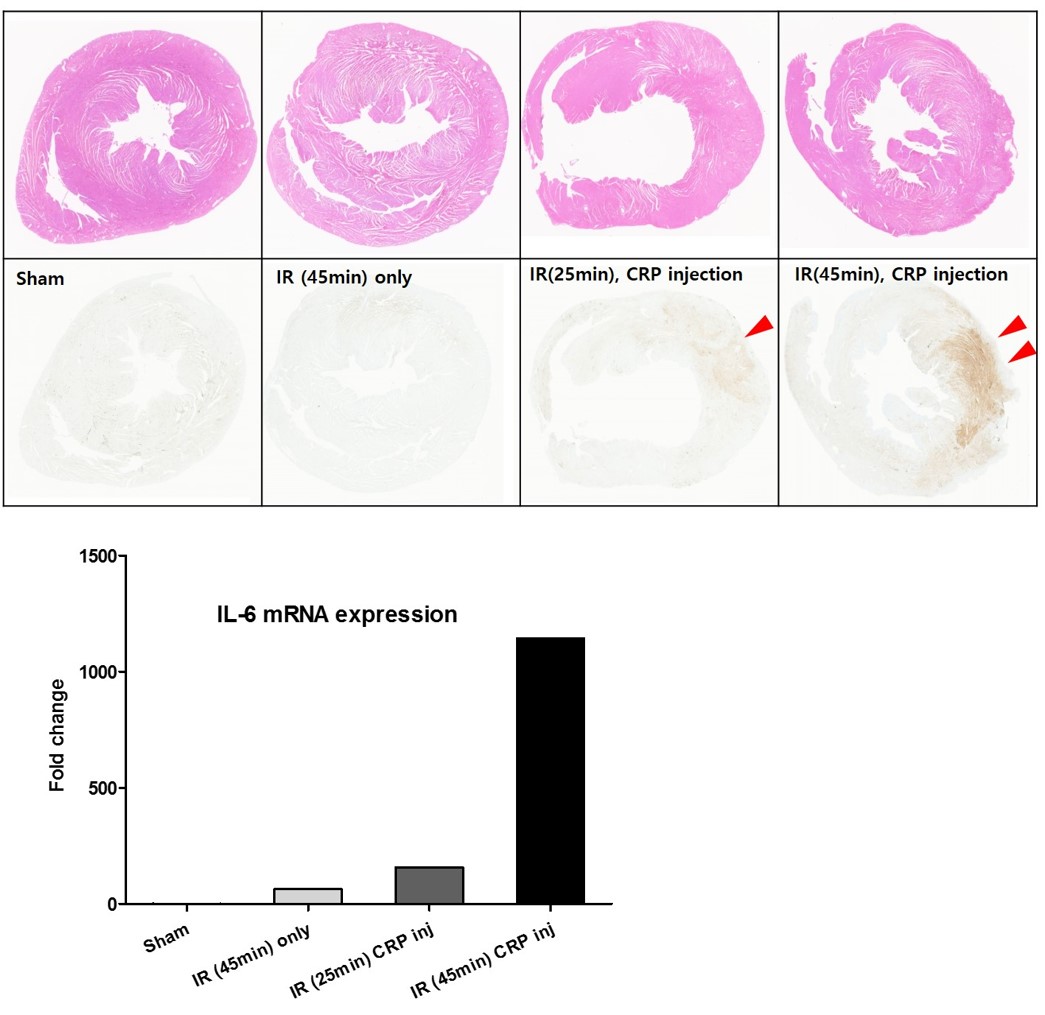
Results : Increased cytoplasmic CRP immunostaining in infarcted area was observed in I/R-CRP group, but not in I/R and sham group (Figure 1). IL-6 mRNA expression was increased in I/R and I/R-CRP group as dose dependent manner (Figure 2). CRP mRNA expression was not detected in rat liver and heart.
Conclusion : CRP immunoreactivity of injured myocardiocyte is a consequence of deposition rather than production of mCRP, and associated with IL-6 mRNA overexpression which has potent proinflammatory role. Therefore, inhibition of monomeric CRP deposition in damaged myocardiocyte could be a new therapeutic target in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Methods : Female Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 250g to 300g were used for in vivo study. Myocardial ischemia was produced by ligation of LAD followed by reperfusion. Because CRP in rat does not activate complement system, we infused 200ug of human CRP (pCRP, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) intravenously at the time of reperfusion. Study groups were (1) sham operation (n=2), (2) ischemia-reperfusion injury without human CRP infusion (I/R, n=1), (3) I/R injury (25minutes of ischemia) with human CRP infusion (I/R-CRP, n=1), and (4) I/R injury (45minutes of ischemia) with human CRP infusion (I/R-CRP, n=1). Immunohistochemistry was conducted with a rabbit polyclonal anti-CRP antibody (1:250 dilution, AbCam,Cambridge, UK). Quantitative RT-PCR was used to determine CRP mRNA and IL-6 mRNA levels in heart and liver.
Results : Increased cytoplasmic CRP immunostaining in infarcted area was observed in I/R-CRP group, but not in I/R and sham group (Figure 1). IL-6 mRNA expression was increased in I/R and I/R-CRP group as dose dependent manner (Figure 2). CRP mRNA expression was not detected in rat liver and heart.
Conclusion : CRP immunoreactivity of injured myocardiocyte is a consequence of deposition rather than production of mCRP, and associated with IL-6 mRNA overexpression which has potent proinflammatory role. Therefore, inhibition of monomeric CRP deposition in damaged myocardiocyte could be a new therapeutic target in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
책임저자: 오세진
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul Municipal Boramae Hospital, Seoul National University Colleage of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
연락처 : 오세진, Tel: 02-870-2295 , E-mail : wpwnn@hanmail.net