초록접수 현황
| 15F-054 | 포스터 발표 |
Prognosis of Lung Cancer Patients Diagnosed with National Health Surveillance
변천성¹, 오중환¹, 리원연², 박일환¹
연세대학교 원주의과대학 원주세브란스기독병원 흉부외과학교실¹, 연세대학교 원주의과대학 원주세브란스기독병원 내과학교실²
Background : National health surveillance with chest X-ray is performing in our country every two years. The present study was performed to evaluate the differences in clinical characteristics and survival outcomes of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) according to detecting the disease by health surveillance with chest X-ray (CXR) or presenting symptoms (SX).
Methods : We identified 294 patients (male/female ratio: 226/68; mean age: 68.7 years old) in tertiary university hospital between Jan 2010 and Dec 2012. The patients were divided into two categories according to method of detection. The clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes were estimated according to CXR group and SX group.
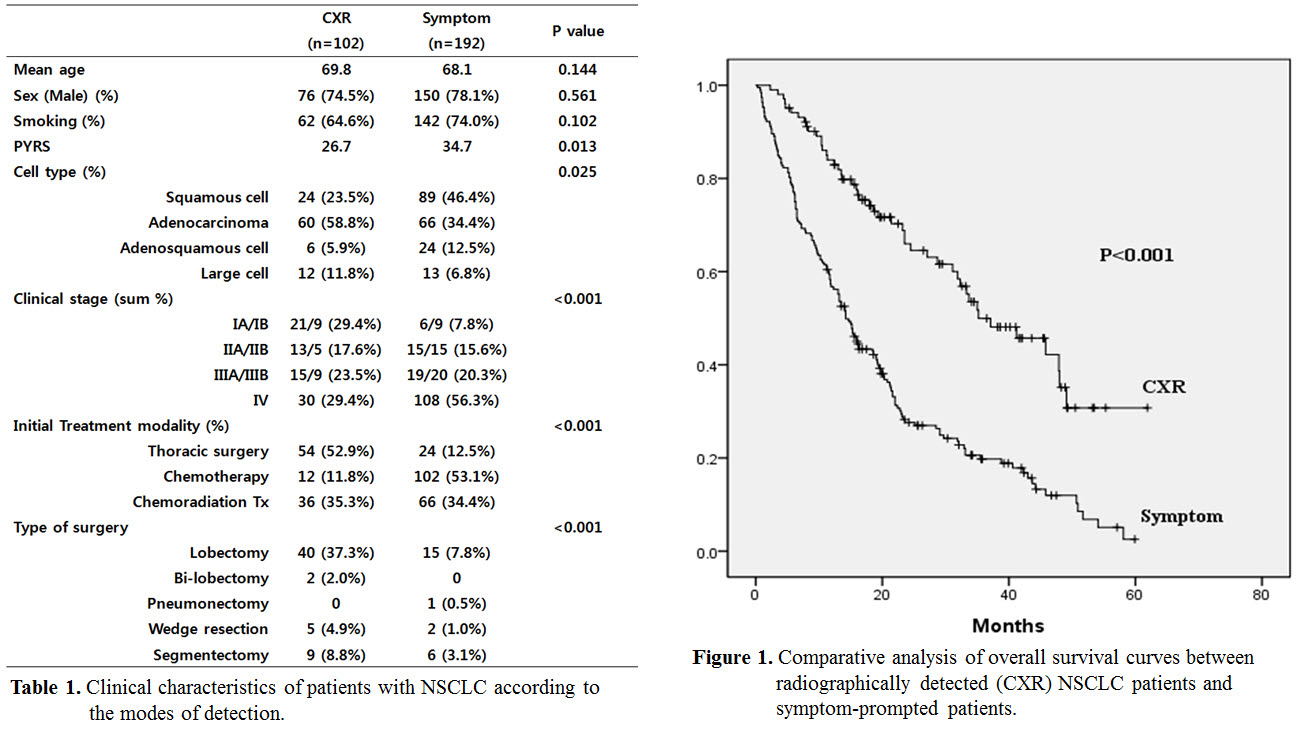
Results : CXR group was 102 patients and SX group was 192 patients. There were significant shift to early TNM stage distribution, cancer cell type, initial treatment modality and type of surgery in the CXR group compared with SX group (table 1). Median survival times were 35.2 months (95% confidence interval (CI): 24.1–46.3) in CXR group, and 14.2 months (95% CI: 12.1–16.3) in SX group. There were statistically significant differences in overall survival between CXR and SX groups (P=0.001) (figure1).
Conclusion : The symptom-prompted patients tend to more advanced squamous cell carcinoma, and most of them treated with chemotherapy or chemoradiation therapy. However, those who diagnosed by National Health Surveillance with chest X ray, there are more early stage adenocarcinoma, and many of them treated by thoracic surgery such as lobectomy. Therefore, Lung cancer screening by national health surveillance with chest X-ray contributed to better clinical outcome in patients with NSCLC.
Methods : We identified 294 patients (male/female ratio: 226/68; mean age: 68.7 years old) in tertiary university hospital between Jan 2010 and Dec 2012. The patients were divided into two categories according to method of detection. The clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes were estimated according to CXR group and SX group.
Results : CXR group was 102 patients and SX group was 192 patients. There were significant shift to early TNM stage distribution, cancer cell type, initial treatment modality and type of surgery in the CXR group compared with SX group (table 1). Median survival times were 35.2 months (95% confidence interval (CI): 24.1–46.3) in CXR group, and 14.2 months (95% CI: 12.1–16.3) in SX group. There were statistically significant differences in overall survival between CXR and SX groups (P=0.001) (figure1).
Conclusion : The symptom-prompted patients tend to more advanced squamous cell carcinoma, and most of them treated with chemotherapy or chemoradiation therapy. However, those who diagnosed by National Health Surveillance with chest X ray, there are more early stage adenocarcinoma, and many of them treated by thoracic surgery such as lobectomy. Therefore, Lung cancer screening by national health surveillance with chest X-ray contributed to better clinical outcome in patients with NSCLC.
책임저자: 박일환
연세대학교 원주의과대학 원주세브란스기독병원 흉부외과학교실
연락처 : 변천성, Tel: 010-3477-7880 , E-mail : csbyun@yonsei.ac.kr