초록접수 현황
| 14F-078 | 구연 발표 |
Classification of Pectus Excavatum by Hierarchical Clustering of Morphologic Parameters Measured in Chest Computed Tomography Scan
최진호, 강창현, 박샘이나, 복진산, 황유화, 이현주, 박인규, 김영태
서울대학교 의과대학 서울대학교병원 흉부외과학교실
Background : To suggest new morphologic classification derived from hierarchical clustering of morphologic parameters measured in chest CT scan and verify clinical relevance of suggested classification.
Methods : Patients who underwent surgical repair (Ravitch or Nuss) of pectus excavatum without history of previous chest surgery were included in this study. Five representative parameters including pectus index (PI), asymmetry index (AI), flatness index (FI), sternal torsion angle (STA), and angle of Louis (AoL) were measured by preoperative chest CT scan. The classification was performed by hierarchical clustering of parameters and its clinical relevance was verified by identifying the association with combined anomalies and additional surgical modification.
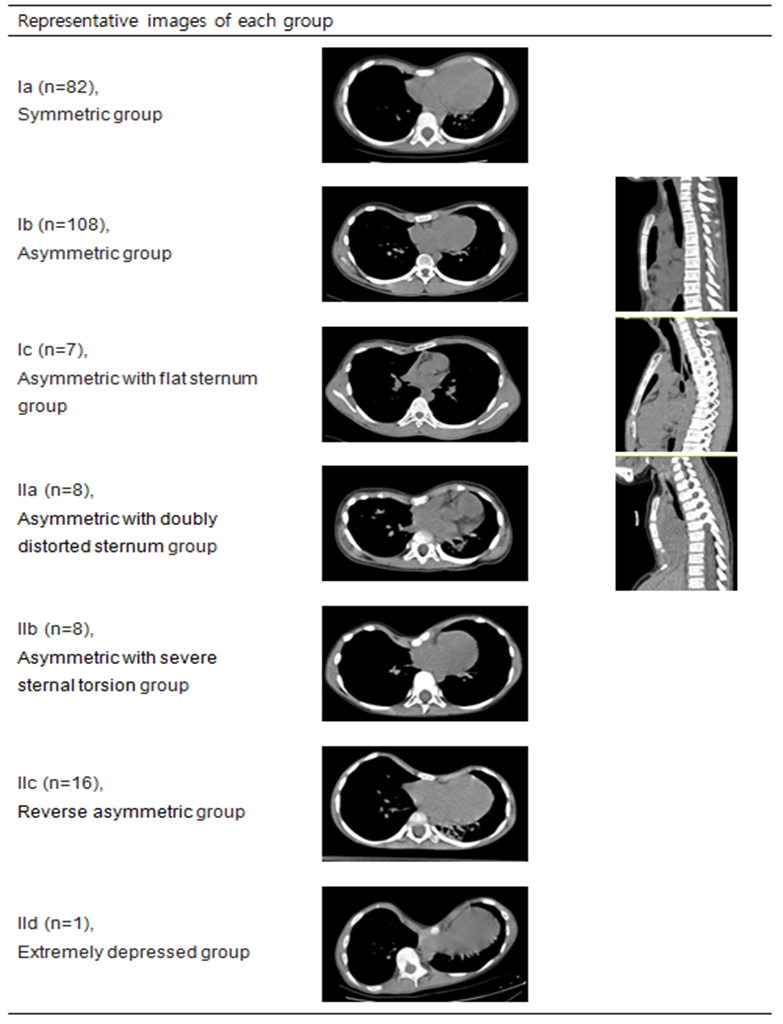
Results : A total of 230 patients who were operated on between January 2001 and August 2013 were included in the study. Hierarchical clustering classified two major groups, typical (group I; n=197) and atypical (group II; n=33). Each major group could be classified into minor groups. Typical major group could be divided in 3 minor groups including Ia (n=82): symmetric group, Ib (n=108): asymmetric group, and Ic (n=7): asymmetric with flat sternum group. Atypical major groups could be classified into 4 minor groups including IIa (n=8): asymmetric with doubly distorted sternum group, IIb (n=8): asymmetric with severe sternal torsion group, IIc (n=16): reverse asymmetric group, and IId (n=1): extremely depressed group. Compared to symmetric group Ia, scoliosis was more common in group IIa (p=0.0008, odd ratio[OR]=10.5, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.7~63.6) and multiple bar insertion was necessary more frequently in group Ic (p=0.001, OR=34.9, 95% CI: 3.9-310.1) and IIb (p=0.007, OR=22.7, 95% CI: 2.3-223.6). The asymmetry of the pectus excavatum was related with STA (p<0.0001, R=0.625) and inversely related with AoL (p=0.013, R=-0.163).
Conclusion : Morphologic classification based on imaging parameters from chest CT scan produced 2 major groups with typical and atypical morphology and 7 minor sub-groups. The classification was clinically relevant in that specific sub-groups were associated with scoliosis and necessity of multiple bar insertion.
Methods : Patients who underwent surgical repair (Ravitch or Nuss) of pectus excavatum without history of previous chest surgery were included in this study. Five representative parameters including pectus index (PI), asymmetry index (AI), flatness index (FI), sternal torsion angle (STA), and angle of Louis (AoL) were measured by preoperative chest CT scan. The classification was performed by hierarchical clustering of parameters and its clinical relevance was verified by identifying the association with combined anomalies and additional surgical modification.
Results : A total of 230 patients who were operated on between January 2001 and August 2013 were included in the study. Hierarchical clustering classified two major groups, typical (group I; n=197) and atypical (group II; n=33). Each major group could be classified into minor groups. Typical major group could be divided in 3 minor groups including Ia (n=82): symmetric group, Ib (n=108): asymmetric group, and Ic (n=7): asymmetric with flat sternum group. Atypical major groups could be classified into 4 minor groups including IIa (n=8): asymmetric with doubly distorted sternum group, IIb (n=8): asymmetric with severe sternal torsion group, IIc (n=16): reverse asymmetric group, and IId (n=1): extremely depressed group. Compared to symmetric group Ia, scoliosis was more common in group IIa (p=0.0008, odd ratio[OR]=10.5, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.7~63.6) and multiple bar insertion was necessary more frequently in group Ic (p=0.001, OR=34.9, 95% CI: 3.9-310.1) and IIb (p=0.007, OR=22.7, 95% CI: 2.3-223.6). The asymmetry of the pectus excavatum was related with STA (p<0.0001, R=0.625) and inversely related with AoL (p=0.013, R=-0.163).
Conclusion : Morphologic classification based on imaging parameters from chest CT scan produced 2 major groups with typical and atypical morphology and 7 minor sub-groups. The classification was clinically relevant in that specific sub-groups were associated with scoliosis and necessity of multiple bar insertion.
책임저자: 강창현
서울대학교 의과대학 서울대학교병원 흉부외과학교실
연락처 : 최진호, Tel: 02-2072-2348 , E-mail : miracleho@gmail.com