초록접수 현황
| 14F-069 | 구연 발표 |
Detecting the Conduit Ischemia by Hypoxia Imaging in Rat Esophagectomy Model
박성용1, 정경영2, 강원준3
아주대학교 의과대학 흉부외과학교실1
, 연세대학교 의과대학 세브란스병원 흉부외과학교실2
, 연세대학교 의과대학 핵의학과학교실3
Background : This study is designed to develop the imaging modality for detecting the ischemia of gastric conduit after esophagectomy using hypoxia imaging.
Methods : Rat esophagectomy model was used with 12-16 weeks old, 300-350g male Sprague-Dawley Rat. In operation group (n=5), partial gastric devascularization was done by ligating the left gastric artery and short gastric arteries and esophagogastric anastomosis was done. In control group (n=3), only incision of esophageal-gastric junction and suture was done without gastric devascularization. Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging was taken on a microPET rodent model scanner, 24 hours after initial operation, with 200uCi 64Cu-diacetyl-bis (N4-methylsemicarbazone) (64Cu-ATSM) and 120mg/kg pimonidazole. Immediately after microPET imaging, autoradiography and immunohistochemistry was done.
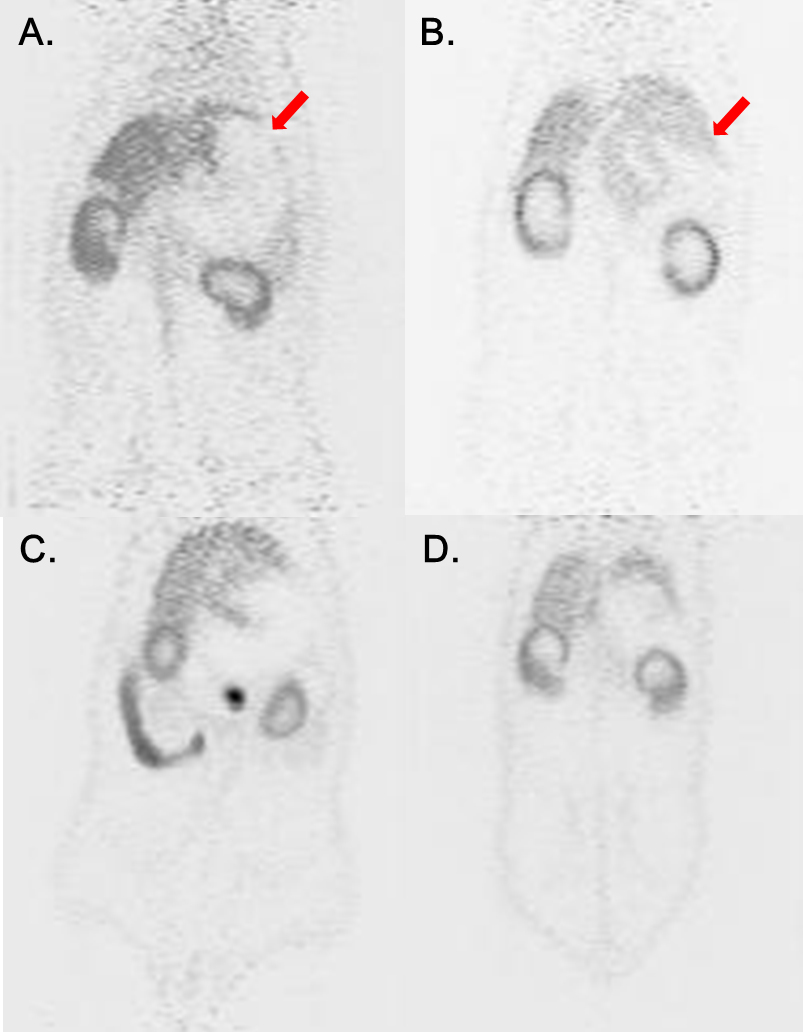
Results : In PET image, the 64Cu-ATSM uptake at fundus area was observed in operation group in images taken 1 and 3 hour image after 64Cu-ATSM injection. In autoradiography, 64Cu-ATSM uptake was observed in operation group, in area of fundus, and it was well correlated to PET image. In immunmohistochemistry, hypoxia inducible factor 1a (HIF-1a) expression and anti-pimonidazole mouse monoclonal IgG1 antibody (MAb1) expression was significantly increased in area of fundus and lesser curvature, compared to greater curvature area in operation group.
Conclusion : Hypoxia PET imaging with 64Cu-ATSM could detect the area of ischemia in rat esophagectomy model. Further clinical study is needed to verify whether hypoxia imaging could be applied in human.
Methods : Rat esophagectomy model was used with 12-16 weeks old, 300-350g male Sprague-Dawley Rat. In operation group (n=5), partial gastric devascularization was done by ligating the left gastric artery and short gastric arteries and esophagogastric anastomosis was done. In control group (n=3), only incision of esophageal-gastric junction and suture was done without gastric devascularization. Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging was taken on a microPET rodent model scanner, 24 hours after initial operation, with 200uCi 64Cu-diacetyl-bis (N4-methylsemicarbazone) (64Cu-ATSM) and 120mg/kg pimonidazole. Immediately after microPET imaging, autoradiography and immunohistochemistry was done.
Results : In PET image, the 64Cu-ATSM uptake at fundus area was observed in operation group in images taken 1 and 3 hour image after 64Cu-ATSM injection. In autoradiography, 64Cu-ATSM uptake was observed in operation group, in area of fundus, and it was well correlated to PET image. In immunmohistochemistry, hypoxia inducible factor 1a (HIF-1a) expression and anti-pimonidazole mouse monoclonal IgG1 antibody (MAb1) expression was significantly increased in area of fundus and lesser curvature, compared to greater curvature area in operation group.
Conclusion : Hypoxia PET imaging with 64Cu-ATSM could detect the area of ischemia in rat esophagectomy model. Further clinical study is needed to verify whether hypoxia imaging could be applied in human.
책임저자: 정경영
연세대학교 의과대학 흉부외과학교실
연락처 : 박성용, Tel: 031-219-5210 , E-mail : psy1117@hanmail.net