초록접수 현황
| 14F-043 | 구연 발표 |
Intraoperative Merged Fluorescence Image-guided Pulmonary Segmentectomy
김현구¹, 오유진², 전옥화¹, 최병현¹, 한국남¹, 김법민², 최영호¹
고려대학교 의과대학 구로병원 흉부외과학교실, 고려대학교 생체의공학과²
Background : Image-guided segmentectomy was introduced for identifying the intersegmental plane during lung cancer surgery. However, the segmentectomy trial using the merged imaging system has not been studied. We performed pulmonary segmentectomy in animal models, using a recently updated version of an intraoperative color and fluorescence merged imaging system (ICFIS). The feasibility of image-guided segmentectomy using the merged system was validated for the first time, and the concentration of fluorescent dye injected was optimized.
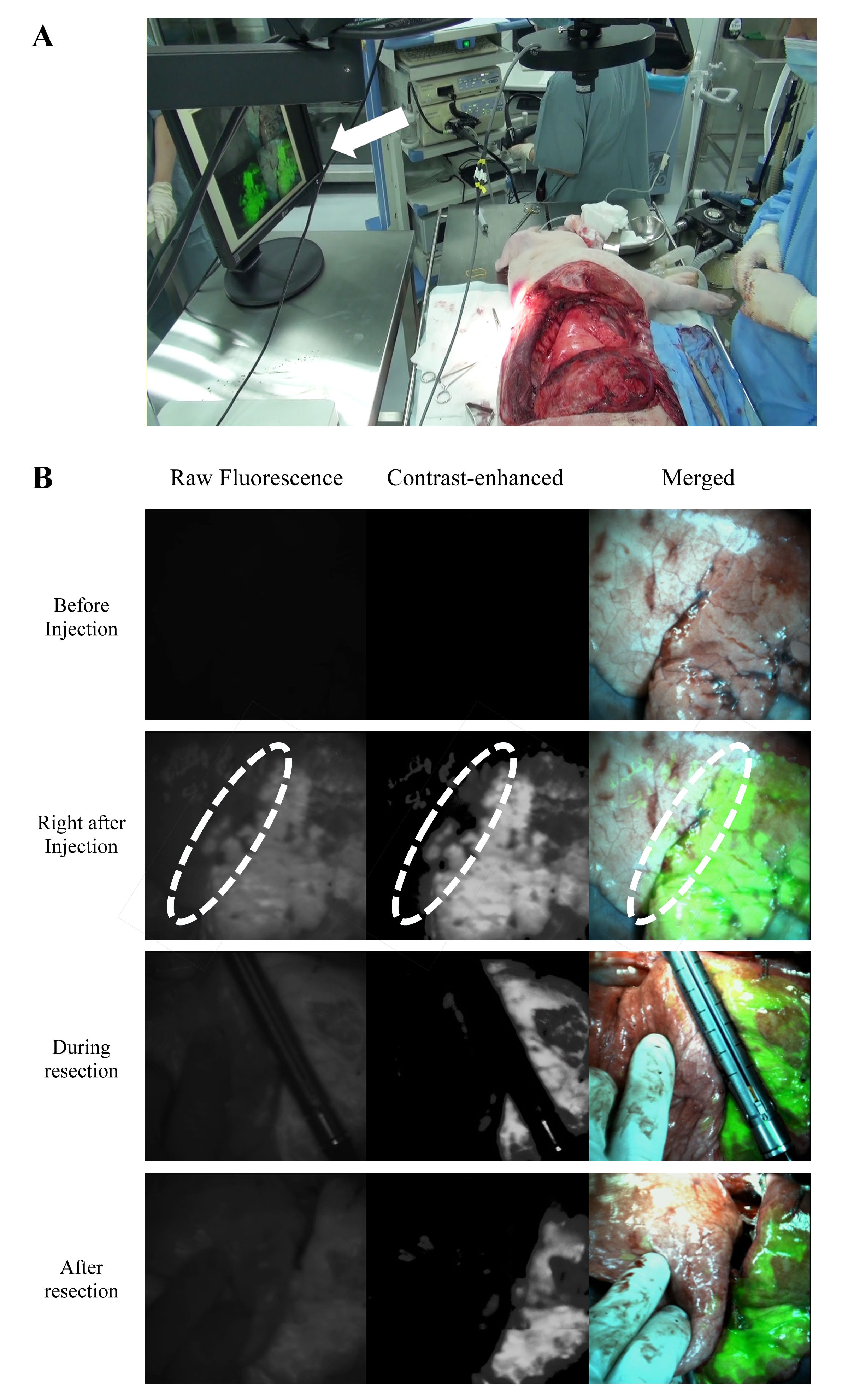
Methods : After ligating the dominant segmental pulmonary artery to the targeted segment, indocyanine green (ICG) was injected intravenously at concentrations of 3.0, 0.6, or 0.3 mg/kg into rabbits. The contrast value between the fluorescence signal of the targeted segment, and the signal of the normal tissue was measured. The optimal ICG dose determined was then administered to pigs, and the image-guided segmentectomy was performed.
Results : Of the three concentrations of ICG injected, 0.6 mg/kg was determined to be optimal, based on the contrast value and the total washout time (3 min). This concentration, when injected in the porcine lung, provided a far greater washout time (over 15 min) owing to slower blood circulation time in the large animal model. Thus, the performance of segmentectomy was guided by merged images without additional marking procedure.
Conclusion : : Image-guided segmentectomy, using the ICFIS and custom contrast-control software, showed prolonged fluorescence washout times that covered the surgical time, and enhanced visualization of surgical margins. Thoracoscopic ICFIS is under development for application in video-assisted thoracoscopic segmentectomy in a future study.
Methods : After ligating the dominant segmental pulmonary artery to the targeted segment, indocyanine green (ICG) was injected intravenously at concentrations of 3.0, 0.6, or 0.3 mg/kg into rabbits. The contrast value between the fluorescence signal of the targeted segment, and the signal of the normal tissue was measured. The optimal ICG dose determined was then administered to pigs, and the image-guided segmentectomy was performed.
Results : Of the three concentrations of ICG injected, 0.6 mg/kg was determined to be optimal, based on the contrast value and the total washout time (3 min). This concentration, when injected in the porcine lung, provided a far greater washout time (over 15 min) owing to slower blood circulation time in the large animal model. Thus, the performance of segmentectomy was guided by merged images without additional marking procedure.
Conclusion : : Image-guided segmentectomy, using the ICFIS and custom contrast-control software, showed prolonged fluorescence washout times that covered the surgical time, and enhanced visualization of surgical margins. Thoracoscopic ICFIS is under development for application in video-assisted thoracoscopic segmentectomy in a future study.
책임저자: 김현구
고려대학교 의과대학 구로병원 흉부외과학교실
연락처 : 김현구, Tel: 02-2626-3106 , E-mail : kimhyunkoo@korea.ac.kr