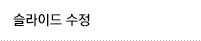초록접수 현황
| 14F-036 | 포스터 발표 |
The Rupture of Right Atrium and Superior Vena Cava Junction in Blunt Thoracic Trauma
변천성, 박일환, 오중환
연세대학교 원주의과대학 흉부외과학교실
Background : Cardiac trauma is common in blunt injuries of the chest. However, survival after a cardiac rupture is rarely encountered clinically, and only a certain percentage of the patients reach the hospital alive. Previous studies have found that the incidence of blunt traumatic cardiac rupture among hospital trauma admissions ranges from approximately 0.16–2%. We report one case of successful treatment of large cardiac rupture due to blunt trauma.
Results : The 41-year male patient came to our emergency center by wheel chair with anterior chest wall blunt trauma due to direct compression of factory machine. The vital sign showed tachycardia and hypotension with alert mental status. Echocardiography demonstrated cardiac tamponade resulting from hemopericardium and large hematoma.
Emergency physician did a subxiphoid pericardial drainage in emergency room. The subxiphoid drainage could relieve cardiac tamponade within minutes thus to gain a better chance to cardiac repair in operative room and to buy time for the operating team for adequate setup.
The operation was performed via mid-sternotomy. The fresh dark blood came after pericardial incision. The cardiac injury sites comprised of superior vena cava/right atrium junction rupture with deep laceration about 7cm into right atrium/ventricular junction. The deep laceration was repaired under Statinsky vascular clamp placed at the base of the right atrial appendage and superior vena cava without assistance of cardiopulmonary bypass. The patient barely recovered stable vital sign after massive volume resuscitation. The postoperative course was uneventful and discharged without sequelae.
Conclusion : The most common feature of blunt traumatic cardiac rupture is cardiac tamponade. However, bleeding ceased for a short time spontaneously by direct compression of hematoma in pericardium. So, surgeon must be aware of massive bleeding after pericardial incision. Most atrial and right ventricular bleeding could be controlled by direct digital pressure or application of a vascular clamp, followed by either oversewn or mattress sutures with pledget reinforcement. Patients with blunt cardiac rupture will continue to be a challenge in critical traumatic care. A high index of suspicion, expeditious diagnostic protocols and appropriate surgical management are essential to a better outcome.
Results : The 41-year male patient came to our emergency center by wheel chair with anterior chest wall blunt trauma due to direct compression of factory machine. The vital sign showed tachycardia and hypotension with alert mental status. Echocardiography demonstrated cardiac tamponade resulting from hemopericardium and large hematoma.
Emergency physician did a subxiphoid pericardial drainage in emergency room. The subxiphoid drainage could relieve cardiac tamponade within minutes thus to gain a better chance to cardiac repair in operative room and to buy time for the operating team for adequate setup.
The operation was performed via mid-sternotomy. The fresh dark blood came after pericardial incision. The cardiac injury sites comprised of superior vena cava/right atrium junction rupture with deep laceration about 7cm into right atrium/ventricular junction. The deep laceration was repaired under Statinsky vascular clamp placed at the base of the right atrial appendage and superior vena cava without assistance of cardiopulmonary bypass. The patient barely recovered stable vital sign after massive volume resuscitation. The postoperative course was uneventful and discharged without sequelae.
Conclusion : The most common feature of blunt traumatic cardiac rupture is cardiac tamponade. However, bleeding ceased for a short time spontaneously by direct compression of hematoma in pericardium. So, surgeon must be aware of massive bleeding after pericardial incision. Most atrial and right ventricular bleeding could be controlled by direct digital pressure or application of a vascular clamp, followed by either oversewn or mattress sutures with pledget reinforcement. Patients with blunt cardiac rupture will continue to be a challenge in critical traumatic care. A high index of suspicion, expeditious diagnostic protocols and appropriate surgical management are essential to a better outcome.
책임저자: 오중환
연세대학교 원주의과대학 흉부외과학교실
연락처 : 변천성, Tel: 033-741-1341 , E-mail : csbyun@yonsei.ac.kr