초록접수 현황
| 14F-262 | 포럼 발표 |
Systemic-pulmonary Shunt Facilitates the Growth of Pulmonary Valve Annulus in ToF
정병권, 박정준, 박천수, 백재숙, 윤태진
울산대학교 의과대학 서울아산병원 흉부외과학교실
Background : Surgical management of tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) has moved toward pulmonary valve annulus (PVA) preservation approaches instead of placing transannular patch (TAP). If the placement of systemic-pulmonary shunt (SPS) facilitates the growth of the PVA, patients with a marginally small PVA, who would have a TAP by a primary repair strategy, could benefit from staged repair strategy in lowering the risk of TAP.
Methods : Among the 347 infants with ToF who underwent surgical correction between January 2004 and December 2013, 29 infants had SPS (29/347, 8%). Serial echocardiographic data prior to ToF repair could be obtained in 168 patients, and changes in PVA z-score (Z) were analyzed.
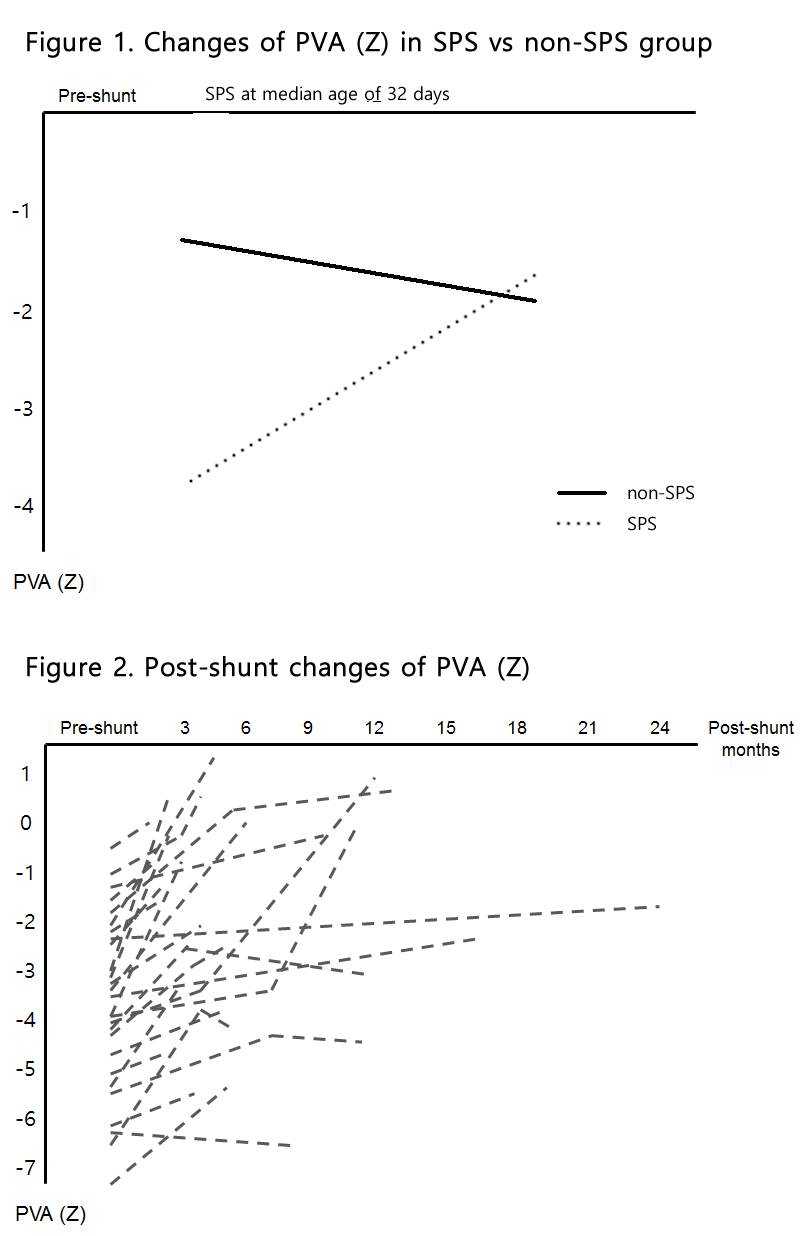
Results : Median age at first echocardiography was 1 day. Pre-shunt PVA (Z) were significantly smaller in patients who would had SPS (-3.68 vs -1.68, P < .01). SPS was performed at the median age of 32 days (range: 5-315 days). PVA (Z) prior to repair increased to -2.02 in SPS group while there was slight decrease in PVA (Z) in non-SPS group showed -2.12 (Figure 1, P < .01). On mixed linear regression, PVA (Z) significantly increased after SPS (Figure 2, P=0.012), while there was no significant change in PVA (Z) in non-SPS group. Repeated measures ANOVA test confirmed inter-group difference significant with P-value of less than 0.01.
Conclusion : SPS faciliates the growth of PVA in ToF. For young infants with a marginally small PVA, placement of SPS may be a better option than attempting primary repair in lowering the risk of TAP.
Methods : Among the 347 infants with ToF who underwent surgical correction between January 2004 and December 2013, 29 infants had SPS (29/347, 8%). Serial echocardiographic data prior to ToF repair could be obtained in 168 patients, and changes in PVA z-score (Z) were analyzed.
Results : Median age at first echocardiography was 1 day. Pre-shunt PVA (Z) were significantly smaller in patients who would had SPS (-3.68 vs -1.68, P < .01). SPS was performed at the median age of 32 days (range: 5-315 days). PVA (Z) prior to repair increased to -2.02 in SPS group while there was slight decrease in PVA (Z) in non-SPS group showed -2.12 (Figure 1, P < .01). On mixed linear regression, PVA (Z) significantly increased after SPS (Figure 2, P=0.012), while there was no significant change in PVA (Z) in non-SPS group. Repeated measures ANOVA test confirmed inter-group difference significant with P-value of less than 0.01.
Conclusion : SPS faciliates the growth of PVA in ToF. For young infants with a marginally small PVA, placement of SPS may be a better option than attempting primary repair in lowering the risk of TAP.
책임저자: 윤태진
울산대학교 의과대학 서울아산병원 흉부외과학교실
연락처 : 정병권, Tel: 02-3010-3580 , E-mail : pogri@naver.com