초록접수 현황
| 14F-026 | 포스터 발표 |
Necrotizing Esophagitis with Emphysematous Gastroenteritis: a Case Report
이준호, 김혁, 김영학, 강정호, 정원상
한양대학교 의과대학 서울병원 흉부외과학교실
목적 : Necrotizing esophagitis (괴사성 식도염)는 매우 드문 질환이며, 정확한 원인은 아직 밝혀지지 않고 있다. 상부 위장관 내시경을 통한 진단시 black, ulcerated, 그리고 necrotic한 양상을 보이며, 병리학적으로도 mucosa 및 submucosa에 necrosis 소견을 보인다. 본원에서는 당뇨를 기저 질환으로 가진 남자 24세 환자의 Emphysematous gastroenteritis (기종성 위장염)과 동반된 Necrotizing esophagitis의 수술적 치료를 통한 호전을 보인 1례를 경험하였기에 이 증례를 보고하고자 한다.
방법 : 남자 24세 환자로 내원 전날부터 발생한 쥐어짜는 양상의 epigastric pain으로 응급실 내원. 2005년 당뇨, 2008년 Kleinfelter syndrome, 2011년 local clinic에서 9개월간 폐결핵 치료 후 완치 판정받았던 History 있음.
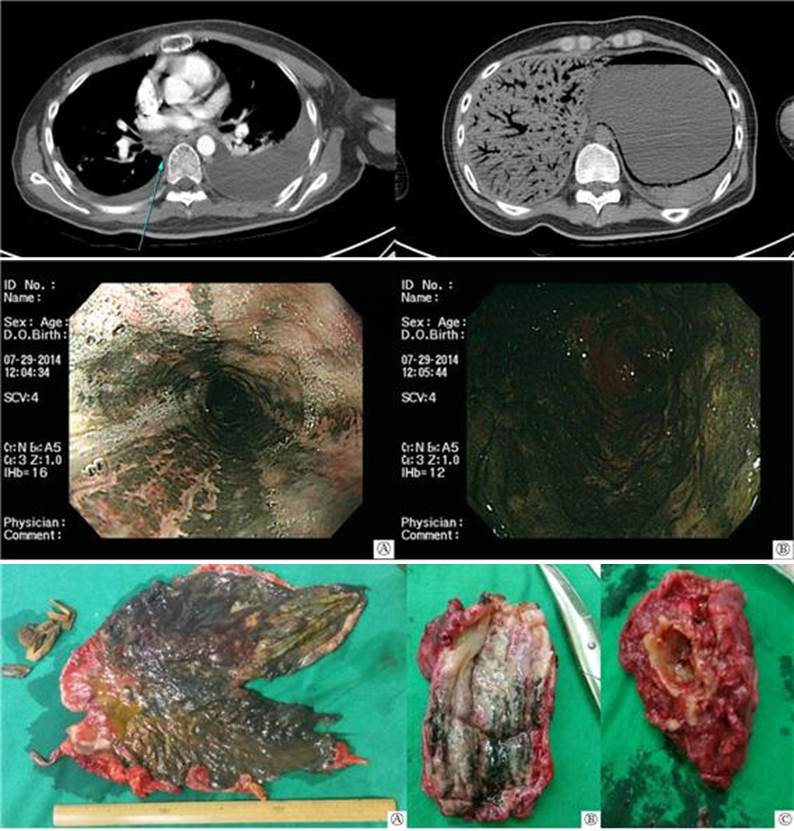
응급실에서 채취한 Laboratory test에서 Ketone 4+, Glucose 919, Creatinine 2.55 및 RUA에서 Ketone 1+ 소견 보여 Diabetic ketoacidosis 진단됨. 응급실에서 시행 및 중환자실 입원 후 익일 추적 관찰한 Abdomen CT에서 Diffuse portal vein gas 및 esophagus부터 duodenum의 2nd portion에 걸쳐 Pneumatosis intestinalis 소견 보임. 3일 후 f/u 한 Chest CT에서 large amount of both pleural effusion과 동반된 diffuse esophageal wall thickening with enlargement of paraesophageal lymph node 소견으로 보아 Necrotizing esophagitis을 시사하며 RLL superior segment에 Pulmonary tuberculosis로 추정되는 cavitary nodule 보임. 동일 c/u 한 Abdomen CT에서는 stomach wall을 따라 보이던 air density는 다소 증가하였으며 edematous wall thickening도 악화되어 Ischemia나 necrosis가 악화중인 것으로 사료됨. 지속되는 fever와 함께 sepsis, panperitonitis 등으로의 진행 가능성 높을 것으로 판단되어 상부 위장관 내시경으로 재확인 후 응급 수술 결정함.
GS에서 Total gastrectomy 및 feeding jejunostomy 시행하였고 gastroduodenal junction까지 necrosis 소견 침범하지 않은 것으로 판단, 장절제는 시행하지 않음. 본과에서는 다음의 수술을 시행함.
#1. Total esophagectomy (Thoracic)
#2. Cervical esophagostomy
#3. Wedge resection, RLL superior segment
#4. Closed thoracostomy, Lt.
결과 : Op findings :
#1. Necrotizing esophagitis due to emphysematous gastroenteritis was extended to mid-esophagus.
#2. A cavitary nodule with color change was palpabled at RLL superior segment.
#3. Moderate amount of right pleural effusion and large amount of left pleural effusion due to secondary change of necrotizing esophagitis were noted.
The result of permanent biopsy :
#1. Esophagus : Necrosis, ulceration
#2. Stomach : Infarction, transmural
#3. Lung nodule, RLL superior segment : Necrotizing granulomatous inflammation, consistent with tuberculosis
결론 : 혈당 조절 등의 내과적 치료를 통해 환자의 증세가 호전된다는 보고도 있으나, 본 case 환자의 경우와 같이 septic shock이나 panperitonitis로의 진행시 life saving을 위한 응급수술 등의 외과적 치료가 고려되어야 할 것으로 사료된다.
대한흉부심장혈관외과학회지에서 소개된 전례가 없는 진단명으로, 수술적 치료를 통해 호전을 보인 환자 1례가 있어 보고함.
방법 : 남자 24세 환자로 내원 전날부터 발생한 쥐어짜는 양상의 epigastric pain으로 응급실 내원. 2005년 당뇨, 2008년 Kleinfelter syndrome, 2011년 local clinic에서 9개월간 폐결핵 치료 후 완치 판정받았던 History 있음.
응급실에서 채취한 Laboratory test에서 Ketone 4+, Glucose 919, Creatinine 2.55 및 RUA에서 Ketone 1+ 소견 보여 Diabetic ketoacidosis 진단됨. 응급실에서 시행 및 중환자실 입원 후 익일 추적 관찰한 Abdomen CT에서 Diffuse portal vein gas 및 esophagus부터 duodenum의 2nd portion에 걸쳐 Pneumatosis intestinalis 소견 보임. 3일 후 f/u 한 Chest CT에서 large amount of both pleural effusion과 동반된 diffuse esophageal wall thickening with enlargement of paraesophageal lymph node 소견으로 보아 Necrotizing esophagitis을 시사하며 RLL superior segment에 Pulmonary tuberculosis로 추정되는 cavitary nodule 보임. 동일 c/u 한 Abdomen CT에서는 stomach wall을 따라 보이던 air density는 다소 증가하였으며 edematous wall thickening도 악화되어 Ischemia나 necrosis가 악화중인 것으로 사료됨. 지속되는 fever와 함께 sepsis, panperitonitis 등으로의 진행 가능성 높을 것으로 판단되어 상부 위장관 내시경으로 재확인 후 응급 수술 결정함.
GS에서 Total gastrectomy 및 feeding jejunostomy 시행하였고 gastroduodenal junction까지 necrosis 소견 침범하지 않은 것으로 판단, 장절제는 시행하지 않음. 본과에서는 다음의 수술을 시행함.
#1. Total esophagectomy (Thoracic)
#2. Cervical esophagostomy
#3. Wedge resection, RLL superior segment
#4. Closed thoracostomy, Lt.
결과 : Op findings :
#1. Necrotizing esophagitis due to emphysematous gastroenteritis was extended to mid-esophagus.
#2. A cavitary nodule with color change was palpabled at RLL superior segment.
#3. Moderate amount of right pleural effusion and large amount of left pleural effusion due to secondary change of necrotizing esophagitis were noted.
The result of permanent biopsy :
#1. Esophagus : Necrosis, ulceration
#2. Stomach : Infarction, transmural
#3. Lung nodule, RLL superior segment : Necrotizing granulomatous inflammation, consistent with tuberculosis
결론 : 혈당 조절 등의 내과적 치료를 통해 환자의 증세가 호전된다는 보고도 있으나, 본 case 환자의 경우와 같이 septic shock이나 panperitonitis로의 진행시 life saving을 위한 응급수술 등의 외과적 치료가 고려되어야 할 것으로 사료된다.
대한흉부심장혈관외과학회지에서 소개된 전례가 없는 진단명으로, 수술적 치료를 통해 호전을 보인 환자 1례가 있어 보고함.
책임저자: 정원상
한양대학교 의과대학 서울병원 흉부외과학교실
연락처 : 이준호, Tel: 02-2290-8470 , E-mail : ps-gamer@hanmail.net