초록접수 현황
| 14F-112 | 포럼 발표 |
Right Thoracotomy Approach as a Safe Alternative to Sternotomy in Redo Mitral Valve Surgery
김홍래, 유재석, 김준범, 정성호, 주석중, 정철현, 이재원
울산대학교 의과대학 서울아산병원 흉부외과학교실
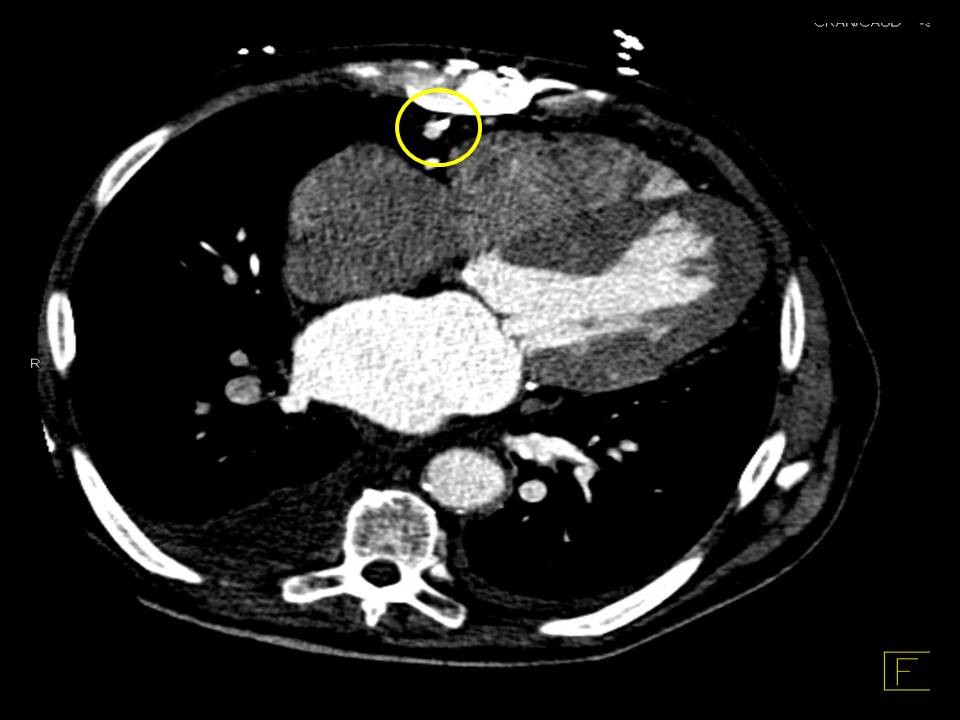
목적 : Redo cardiac surgery through sternotomy carries a higher operative risk such as major vessel injury, wound infection, and stroke, especially when there is a severe pericardial adhesion or patent coronary arterial bypass grafts (Figure). Owing to the specific anatomical position of the mitral valve, right thoracotomy approach can remove the need for sternal reentry and excessive adhesiolysis in redo mitral valve surgery. This study aimed to review our experience of redo mitral valve surgery through a right thoracotomy approach.
방법 : Between May 2006 and August 2014, 45 patients (age 52.4 ± 12.9 years; 12 male patients (26.7%)) underwent redo mitral valve surgeries through a right thoracotomy approach at Asan Medical Center. Mitral replacement was performed with or without concomitant procedures: tricuspid repair in 20 (44.4%) and Maze procedure in 10(22.2%).
결과 : Previous cardiac surgeries included CABG in 2 patients (4.4%), mitral valve repair or replacement in 41 patients (91.1%), aortic valve procedures in 5 patients (12.1%), and other procedures in 3 patients (6.6%). Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) was carried out through peripheral femoro-femoral cannulation in 97.8% of the patients; ascending aortic cannulation was used in only 1 patient (2.2%). Cardioplegic arrest with transthoracic aortic crossclamping (ACC) was performed in 41 patients (91.1%), and hypothermic fibrillatory arrest strategy was used in 4(8.9%) for whom securing the ACC site was impossible. The mean CPB and ACC times were 166.2±44.4 and 93.5±30.9 minutes, respectively.
There was no operative death. Operative complications occurred in 8 patients (17.8%), which included postoperative bleeding requiring re-exploration in 5 patients (11.1%), low cardiac output requiring mechanical support in 1 (2.2%), and transient ischemic attack in 1(2.2%). However, there was no permanent stroke.
결론 : A right thoracotomy approach at the time of redo mitral valve surgery might be a good alternative to sternotomy in terms of its excellent exposure of the mitral valve with limited dissection of adhesions and low risk of operative complications.
방법 : Between May 2006 and August 2014, 45 patients (age 52.4 ± 12.9 years; 12 male patients (26.7%)) underwent redo mitral valve surgeries through a right thoracotomy approach at Asan Medical Center. Mitral replacement was performed with or without concomitant procedures: tricuspid repair in 20 (44.4%) and Maze procedure in 10(22.2%).
결과 : Previous cardiac surgeries included CABG in 2 patients (4.4%), mitral valve repair or replacement in 41 patients (91.1%), aortic valve procedures in 5 patients (12.1%), and other procedures in 3 patients (6.6%). Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) was carried out through peripheral femoro-femoral cannulation in 97.8% of the patients; ascending aortic cannulation was used in only 1 patient (2.2%). Cardioplegic arrest with transthoracic aortic crossclamping (ACC) was performed in 41 patients (91.1%), and hypothermic fibrillatory arrest strategy was used in 4(8.9%) for whom securing the ACC site was impossible. The mean CPB and ACC times were 166.2±44.4 and 93.5±30.9 minutes, respectively.
There was no operative death. Operative complications occurred in 8 patients (17.8%), which included postoperative bleeding requiring re-exploration in 5 patients (11.1%), low cardiac output requiring mechanical support in 1 (2.2%), and transient ischemic attack in 1(2.2%). However, there was no permanent stroke.
결론 : A right thoracotomy approach at the time of redo mitral valve surgery might be a good alternative to sternotomy in terms of its excellent exposure of the mitral valve with limited dissection of adhesions and low risk of operative complications.
책임저자: 이재원
울산대학교 의과대학 서울아산병원 흉부외과학교실
연락처 : 김홍래, Tel: 02-3010-0089 , E-mail : khrjsk@gmail.com